Why Are The Elderly More Susceptible To Illness?
Learn why the elderly are more susceptible to illness and how to prevent it. Tips for staying healthy in your golden years.
.jpg)
Why Are The Elderly More Susceptible To Illness?
To understand why the elderly are more susceptible to illness, it is important to explore the link between aging and immune system decline. As individuals age, their immune system undergoes changes that can impact its ability to defend against infections and diseases. In this section, we will provide an overview of the aging process and its impact on the immune system, as well as an understanding of the immune system itself.

The Aging Process and its Impact on the Immune System
Aging is a natural process that affects every system in the body, including the immune system. As individuals age, the immune system undergoes a phenomenon known as immunosenescence, which refers to the age-related decline in immune function. This decline can make the elderly more susceptible to infections, diseases, and even certain cancers.
Immunosenescence is characterized by a gradual deterioration of the immune system's ability to respond effectively to pathogens. The immune system becomes less efficient in recognizing and eliminating harmful substances, leading to an increased risk of infections. The decline in immune function can also affect the body's ability to mount an appropriate immune response, resulting in slower healing and recovery.
Understanding the Immune System
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful invaders, such as bacteria, viruses, and toxins. It is comprised of two main components: the innate immune system and the adaptive immune system.
The innate immune system is the body's first line of defense and provides immediate, nonspecific protection against a wide range of pathogens. It includes physical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes, as well as immune cells such as natural killer cells and phagocytes.
The adaptive immune system, on the other hand, is a more specialized defense mechanism that develops over time. It is characterized by the production of specific antibodies and immune cells that target specific pathogens. The adaptive immune system has memory, allowing it to recognize and respond more effectively to previously encountered pathogens.
As individuals age, both components of the immune system are impacted. The innate immune system may become less efficient at recognizing and eliminating pathogens, while the adaptive immune system may exhibit reduced responsiveness and slower production of antibodies. These changes can contribute to the increased susceptibility to infections and diseases observed in the elderly.
Understanding the aging process and the impact it has on the immune system is crucial for caregivers and family caregivers of elderly individuals. By recognizing the unique challenges faced by the aging immune system, appropriate measures can be taken to support and maintain the health of the elderly.
How Age Affects the Immune System?
As individuals age, their immune system undergoes changes that can lead to a decline in its effectiveness. Understanding how age affects the immune system is key to comprehending why the elderly are more susceptible to illness. Let's explore the changes in the immune system with age and the factors contributing to immune system decline.
Changes in the Immune System with Age
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful pathogens. With age, the immune system undergoes several changes, including:
- Reduced immune cell function: As individuals age, the production and function of immune cells, such as T cells and B cells, may decrease. This can impact the immune system's ability to recognize and eliminate pathogens effectively.
- Decreased response to vaccines: The elderly may experience a reduced response to vaccines, which can make them more susceptible to infections. This is due to the decline in immune cell function and the diminished production of antibodies.
- Increased inflammation: Aging is associated with chronic low-grade inflammation, known as inflammaging. This persistent inflammation can disrupt the immune system's balance and impair its ability to respond appropriately to infections.
- Altered immune signaling: Communication between immune cells becomes less efficient with age. This can result in a delayed or weakened immune response, making it harder for the elderly to fight off infections.
Factors Contributing to Immune System Decline
Several factors contribute to the decline of the immune system as individuals age. These include:
- Immunosenescence: Immunosenescence refers to the age-related changes in the immune system. It is influenced by genetic factors, lifestyle choices, and environmental exposures. Immunosenescence can lead to a less responsive immune system, making the elderly more vulnerable to infections.
- Chronic conditions and medications: Chronic conditions, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, can impact immune function. Additionally, certain medications, such as immunosuppressants used in transplant patients, can further weaken the immune system.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Inadequate nutrition can compromise immune function. The elderly may be at a higher risk of nutrient deficiencies, which can impair the functioning of immune cells.
- Stress and psychological factors: Chronic stress and psychological factors, such as depression and loneliness, can negatively affect the immune system. These factors can contribute to immune system decline and increase susceptibility to illness.
Understanding the changes in the immune system with age and the factors contributing to its decline is crucial for caregivers and family caregivers of the elderly. By recognizing the vulnerabilities of the immune system in the elderly, appropriate measures can be taken to support their overall health and well-being.
Consequences of Immune System Decline
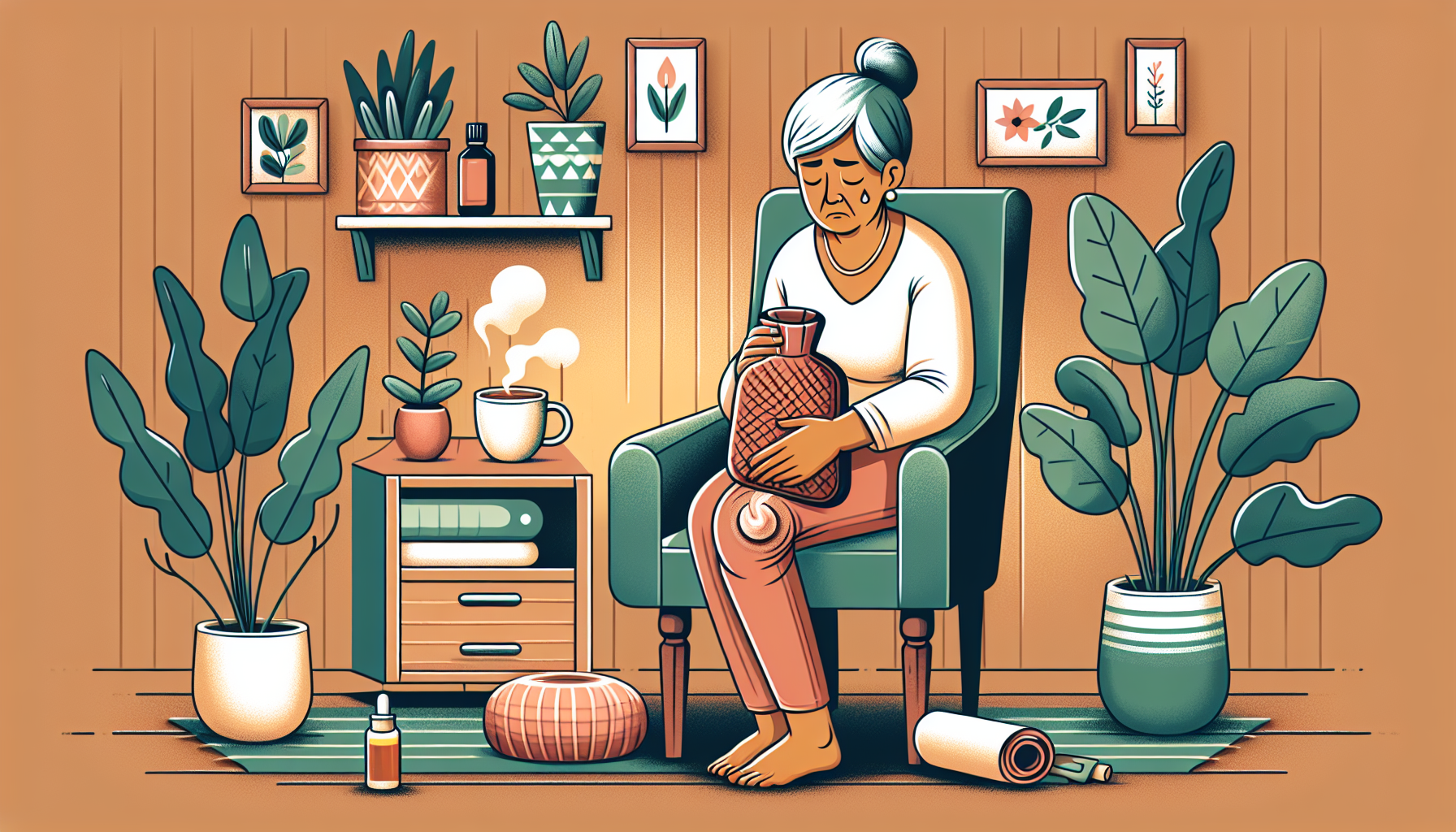
As the immune system undergoes changes with age, there are several significant consequences that can impact the health and well-being of elderly individuals. Two key consequences of immune system decline are increased susceptibility to infections and slower healing and recovery.
Increased Susceptibility to Infections
One of the most notable consequences of immune system decline in the elderly is an increased susceptibility to infections. As the immune system weakens with age, its ability to fight off pathogens and foreign invaders becomes compromised. This makes older adults more vulnerable to common infections such as respiratory infections, urinary tract infections, and influenza.
The decline in immune function, often referred to as age-related immune system dysfunction or immunosenescence, can lead to a decreased response to vaccines and a reduced ability to produce antibodies. This means that the elderly may not mount as strong of an immune response to infections or vaccinations compared to younger individuals.
To mitigate the risk of infection, it is crucial for caregivers and healthcare professionals to promote preventative measures such as regular handwashing, maintaining a clean environment, and practicing good respiratory hygiene. Additionally, ensuring that elderly individuals receive appropriate vaccinations, including annual influenza vaccines and pneumococcal vaccines, can help to reduce the likelihood of developing infections.
Slower Healing and Recovery
Another consequence of immune system decline in the elderly is slower healing and recovery. The immune system plays a crucial role in the body's ability to heal wounds and repair damaged tissues. However, with age, the immune response becomes less efficient, resulting in delayed healing and prolonged recovery times.
The cellular and molecular changes that occur in the immune system with age, often referred to as age-related decline in immune function, can impair the inflammatory response necessary for effective healing. This can lead to chronic wounds, increased susceptibility to infections at the site of injury, and delayed recovery from illnesses or surgical procedures.
To support healing and recovery in the elderly, it is important to provide proper wound care, including regular cleaning and dressing changes. Nutritional support is also crucial, as adequate intake of protein, vitamins, and minerals is essential for tissue repair. Collaborating with healthcare professionals, such as wound care specialists or physical therapists, can help develop personalized care plans to optimize healing and recovery.
By understanding the consequences of immune system decline in the elderly, caregivers and family members can take proactive steps to protect the health and well-being of their loved ones. By implementing preventive measures, promoting good hygiene practices, and addressing the specific needs of older adults, the impact of immune system decline on susceptibility to infections and healing can be effectively managed.
Strategies for Boosting Immune Health in the Elderly
As individuals age, their immune system undergoes changes that can lead to a decline in its effectiveness. However, there are strategies that can be implemented to help boost immune health in the elderly. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, ensuring vaccinations and immunizations are up to date, and focusing on proper nutrition and supplementation, caregivers can play a crucial role in supporting the immune health of their elderly loved ones.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Encouraging and promoting healthy lifestyle habits is essential in supporting immune health in the elderly. Some key habits to focus on include:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity helps to improve overall health and strengthen the immune system. Encourage your loved ones to engage in activities they enjoy, such as walking, swimming, or gentle yoga.
- Sufficient Sleep: A good night's sleep is vital for immune function. Encourage a consistent sleep schedule and create a comfortable sleep environment to promote quality sleep.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system. Encourage stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies and activities that bring joy.
- Smoking Cessation: If your loved one is a smoker, it's crucial to support them in quitting. Smoking compromises immune function and increases the risk of respiratory infections.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can impair immune function. Encourage moderation or avoidance of alcohol to support immune health.
Vaccinations and Immunizations
Ensuring that vaccinations and immunizations are up to date is another important aspect of supporting immune health in the elderly. Vaccines can help protect against various infections and diseases that can be particularly severe in older adults. Common vaccines that are recommended for the elderly include:
Consult with healthcare professionals to ensure that your loved one is up to date with their vaccinations and immunizations.
Proper Nutrition and Supplementation
Proper nutrition plays a significant role in supporting immune health. A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can help strengthen the immune system. Encourage your loved one to consume a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, fruits and vegetables support immune function. Aim for a colorful variety, as different colors indicate different nutrient profiles.
- Protein: Adequate protein intake is vital for immune health. Include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, legumes, and dairy products in the diet.
- Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread, which provide essential nutrients and dietary fiber.
- Healthy Fats: Include sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, which offer anti-inflammatory properties.
In some cases, supplementation may be recommended to address specific nutrient deficiencies. Consult with healthcare professionals to determine if any supplements are necessary.
By implementing these strategies, caregivers can help support the immune health of their elderly loved ones. Remember, it's important to collaborate with healthcare professionals to ensure the best approach tailored to individual needs.
Supporting Elderly Individuals with a Weakened Immune System
As the immune system naturally weakens with age, it's important to provide support and create an environment that promotes the health and well-being of elderly individuals. By implementing certain strategies, caregivers can help boost the immune system and minimize the risk of infections and illnesses. Here are a few ways to support elderly individuals with a weakened immune system:
Encouraging a Healthy Environment
Creating a healthy environment is crucial for maintaining the overall well-being of elderly individuals with a weakened immune system. This involves promoting good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing and disinfecting frequently touched surfaces. Providing a clean and clutter-free living space can help reduce the exposure to germs and pathogens.
In addition, ensuring proper ventilation and air circulation can help minimize the spread of airborne infections. Encourage fresh air circulation by opening windows or using fans. Regularly cleaning and maintaining air filters can also contribute to a healthier environment.
Providing Emotional Support
Emotional well-being plays a significant role in supporting the immune system. Elderly individuals may experience feelings of loneliness, stress, or anxiety, which can have an impact on their overall health. Providing emotional support and companionship can help boost their mood and improve their immune function.
Engage in meaningful conversations, activities, and hobbies to keep their spirits high. Encourage regular social interactions, whether through family visits, phone calls, or virtual connections. By fostering a positive and supportive environment, you can contribute to their emotional well-being and indirectly support their immune system.
Collaborating with Healthcare Professionals
Collaboration with healthcare professionals is essential in supporting elderly individuals with a weakened immune system. Regular check-ups and consultations with healthcare providers can help identify any underlying health conditions or medical issues that may compromise their immune function.
Ensure that they receive recommended vaccinations and immunizations to protect against preventable diseases. Stay updated on the latest recommendations from healthcare professionals regarding vaccinations for the elderly.
Additionally, healthcare professionals can provide guidance on proper nutrition and supplementation to support immune health. Proper nutrition is vital for maintaining a strong immune system. Consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to develop a well-balanced diet plan that meets their specific nutritional needs.
By encouraging a healthy environment, providing emotional support, and collaborating with healthcare professionals, caregivers can effectively support elderly individuals with a weakened immune system. These strategies can contribute to their overall well-being and minimize the risk of infections and illnesses. Remember, every small effort counts in maintaining the health and happiness of our loved ones.
FAQs
Is it true that the elderly have weaker immune systems than younger adults?
Yes. As we age, our immune system undergoes changes that impact how it responds to infections and diseases. The ability of our immune system to produce new immune cells declines, while the number of cells that are less effective in fighting infections increases. This means that older adults are more likely to contract infections and illnesses, and once they do, they may take longer to recover.
Are there lifestyle factors that can impact the susceptibility of the elderly to illness?
Yes. In addition to changes in the immune system, there are also lifestyle factors that can impact the susceptibility of the elderly to illness. For instance, as we age, we may become less physically active and spend more time indoors, which can increase our risk of infection. Furthermore, poor nutrition and stress can also weaken the immune system, making it more difficult to fight off infections.
What steps can be taken to help prevent illness in older adults?
Prevention is key when it comes to keeping the elderly healthy. There are a number of steps that can be taken to help reduce the risk of illness in older adults:
- Practice good hygiene: Washing hands frequently, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and keeping surfaces clean can help reduce the spread of germs.
- Get vaccinated: Vaccines can help prevent illnesses like influenza and pneumonia, which can be particularly dangerous for older adults.
- Stay active: Regular exercise can help boost the immune system and reduce the risk of illness.
- Eat a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can provide the nutrients needed to support a healthy immune system.
- Manage stress: Stress can weaken the immune system, so it's important to find ways to manage stress, such as meditation, yoga, or talking to a therapist.
What treatments are available for illnesses in older adults?
Older adults may require more aggressive treatment for infections and illnesses than younger individuals. Antibiotics, antiviral medications, and other treatments may need to be used to help prevent complications and speed up recovery. It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment of any illness or infection.
Summary
The elderly are more susceptible to illness due to changes in the immune system and lifestyle factors. However, there are steps that can be taken to help reduce the risk of illness and keep older adults healthy. By practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated, staying active, eating a healthy diet, and managing stress, older adults can help support their immune system and reduce the risk of illness.