Technology Integration for Remote Monitoring in Home Care
Learn the potential benefits of technology integration for remote monitoring in home care.

Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote patient monitoring is a valuable tool in the field of healthcare that allows providers to monitor and manage acute and chronic conditions from the comfort of a patient's own home. By utilizing remote monitoring technologies, healthcare practitioners can remotely track and analyze certain aspects of a patient's health, reducing the need for frequent travel and minimizing infection risks [1].
Benefits of Remote Monitoring
There are numerous benefits associated with remote patient monitoring. By implementing remote monitoring technologies, healthcare providers can:
Challenges of Remote Monitoring
While remote patient monitoring offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges that need to be addressed. Some of the challenges include:
By addressing these challenges and leveraging the benefits of remote patient monitoring, healthcare practitioners can enhance patient care, improve health outcomes, and optimize the delivery of healthcare services.

Utilizing Remote Monitoring Technologies
To enhance the quality of care provided in home settings, remote monitoring technologies play a vital role. These technologies enable healthcare providers to remotely monitor patients' health parameters and make informed decisions based on real-time data. In this section, we will explore two key aspects of remote monitoring technologies: remote monitoring devices and wearable devices for health monitoring.
Remote Monitoring Devices
Remote monitoring devices are essential tools that provide valuable insights into a patient's day-to-day routine, helping healthcare providers understand how daily activities affect health and symptoms. These devices can track various health parameters, such as steps, heart rate, fall risk, sleep, blood pressure, glucose, weight, and stress. By continuously monitoring these parameters, remote monitoring devices offer a comprehensive view of the patient's health status, enabling informed treatment planning.
Common remote monitoring devices used in home care include:
These devices are instrumental in managing conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), congestive heart failure (CHF), and more. By remotely monitoring these health parameters, healthcare providers can track patient health and make informed decisions, even from a distance.
Wearable Devices for Health Monitoring
Wearable devices have gained significant popularity in remote monitoring due to their convenience and ability to provide real-time health data. These devices are typically worn on the body and use sensors to collect and transmit health information to healthcare providers. Wearables can track a range of health parameters, including heart rate, sleep patterns, activity levels, and more.
By wearing these devices, patients can actively engage with their health on a daily basis, leading to improved health outcomes. Healthcare providers can gain valuable insights into the patient's overall well-being and identify any changes or abnormalities that may require attention [2].
Wearable devices for health monitoring include fitness trackers, smartwatches, and other specialized devices designed for specific health conditions. These devices offer the convenience of continuous monitoring, allowing caregivers and healthcare providers to track health trends, detect early warning signs, and intervene as necessary.
By utilizing remote monitoring devices and wearable devices for health monitoring, healthcare providers can extend their care beyond traditional settings and actively monitor patients' health remotely. This proactive approach enables timely interventions and personalized care, ultimately improving patient outcomes and enhancing the overall quality of home care.
Telehealth Integration for Remote Monitoring
In the realm of remote monitoring, the integration of telehealth services plays a significant role in enhancing patient care. Telehealth and remote monitoring synergize to provide efficient and effective healthcare solutions for patients, particularly those who require monitoring for specific health conditions or face challenges with travel. Let's explore the synergy between telehealth and remote monitoring, as well as the concept of remote physiologic monitoring (RPM).
Telehealth and Remote Monitoring Synergy
Telehealth and remote monitoring are increasingly popular options that pair well together, allowing healthcare providers to manage acute and chronic conditions while reducing patients' travel costs and infection risks associated with in-person visits. By utilizing telehealth technologies, healthcare professionals can remotely monitor certain aspects of a patient's health from the comfort of their own home, ensuring continuous care and timely intervention when required.
The synergy between telehealth and remote monitoring enables real-time data transmission and analysis, empowering healthcare providers to make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information. Through telehealth platforms, patients can communicate with their healthcare providers, share vital health data, and receive personalized guidance, all while being in the familiar surroundings of their own home.
Remote Physiologic Monitoring (RPM)
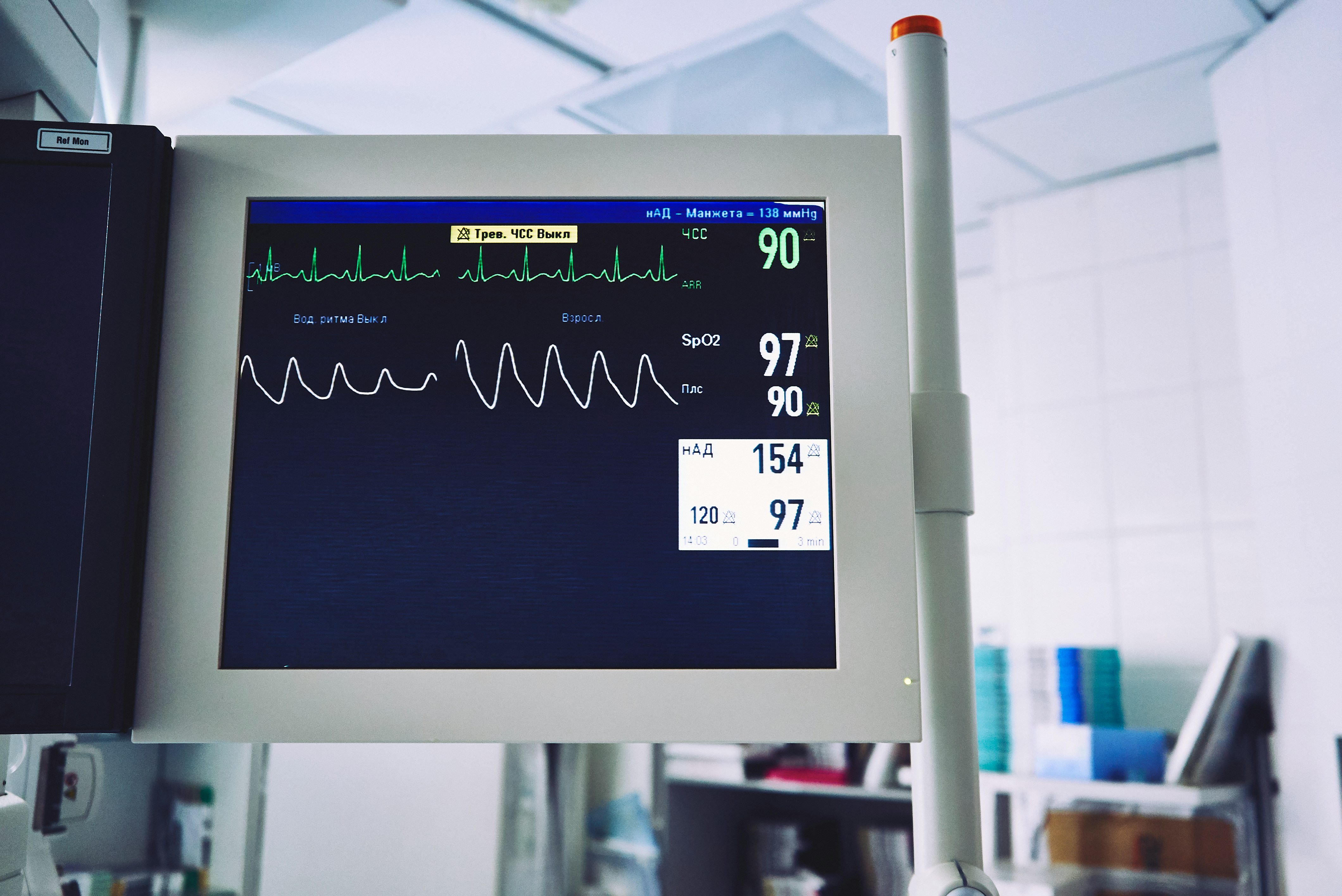
Remote physiologic monitoring (RPM), also known as telemonitoring, involves the non-face-to-face monitoring and analysis of physiologic factors. RPM allows healthcare practitioners to gather real-time information on the physiological conditions of patients, even from a distance.
RPM often utilizes remote patient monitoring devices, including wearable devices, to provide insights into a patient's day-to-day routine and health status. These wearable devices can track various health parameters such as steps taken, heart rate, fall risk, sleep patterns, blood pressure, glucose levels, weight, and stress levels, offering a comprehensive view of the patient's overall health.
The American Heart Association recommends remote monitoring of vital signs for patients with conditions such as hypertension, as it enhances patient engagement, adherence to treatment plans, and expands physician reach without the need for in-person visits. RPM has been historically used to measure symptoms of chronic conditions such as cardiac diseases, diabetes, and asthma, often through wearable devices like Holter monitors for heart rhythm measurement.
By integrating telehealth and RPM, healthcare practitioners can remotely monitor patients' health conditions, detect potential issues in real-time, and intervene when necessary, ensuring timely and proactive care. The ability to monitor patients remotely not only enhances patient outcomes but also reduces the burden on healthcare systems and promotes patient convenience and satisfaction.
The integration of telehealth and remote monitoring facilitates a transformative approach to healthcare delivery, empowering patients to actively participate in their care while receiving necessary support and guidance from healthcare professionals, all from the comfort and convenience of their own homes.
Healthcare Practitioners' Perspectives on Remote Monitoring
To gain a comprehensive understanding of remote monitoring in home care, it is essential to consider the perspectives of healthcare practitioners. Their experiences and opinions provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and challenges of implementing remote patient monitoring (RPM) technologies.
Practitioners' Experiences with RPM
Healthcare practitioners have had varying experiences with RPM, also referred to as telemonitoring. According to the NCBI, there is a consensus among practitioners that telemonitoring strategies will become increasingly relevant in healthcare. RPM allows practitioners to gather real-time information on the physiological conditions of patients, enabling them to provide timely and personalized care.
Studies have shown the benefits of remote patient monitoring in managing diseases like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and congestive heart failure (CHF). These studies have demonstrated positive outcomes, including reduced emergency department visits, decreased hospital readmissions, and shorter hospital stays [3]. This highlights the potential of RPM to improve patient outcomes and enhance the overall effectiveness of healthcare delivery.
However, it is important to acknowledge that there are challenges associated with implementing RPM. Practitioners may experience an increased workload due to the continuous monitoring and management of patient data. Privacy concerns, data accuracy, and financial burdens are also important factors to consider when integrating remote monitoring technologies [4]. Despite these challenges, healthcare practitioners generally believe that RPM is feasible and recognize its potential in providing better care to patients.
Opinions on Telemonitoring Technologies
The opinions of healthcare practitioners on telemonitoring technologies are crucial as telemedicine and remote monitoring become more relevant in today's society. The ability to remotely monitor patients and gather real-time data allows practitioners to provide more personalized care, make informed decisions, and intervene promptly when necessary.
Telehealth, which encompasses telemonitoring, has become a rapidly growing sector of healthcare delivery systems. Previous studies have shown evidence that telehealth tools and services increase the overall effectiveness of physicians in counseling patients with chronic conditions, providing psychotherapy support for behavioral interventions, and remotely monitoring patients. This further highlights the positive impact of telemonitoring technologies on healthcare.
While practitioners generally have a positive outlook on telemonitoring technologies, it is important to address their concerns and challenges. Continuous improvement in technology, data security measures, and addressing the workload implications are areas that need attention to ensure the successful integration of telemonitoring into healthcare practices.
By considering the experiences and opinions of healthcare practitioners, we can gain valuable insights into the benefits and challenges of remote monitoring technologies. This knowledge can help inform the development and implementation of effective remote monitoring strategies, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes in home care settings.
Smart Home Health Technologies
In the realm of remote monitoring in home care, smart home health technologies (SHHTs) play a significant role in enabling aging-in-place and promoting independence for older adults. A systematic review of empirical peer-reviewed articles highlighted the benefits and barriers of utilizing SHHTs from the perspective of older persons and their caregivers. Let's explore the benefits and barriers associated with these technologies.
Benefits of SHHTs
SHHTs have proven to be valuable tools in the care of older persons, particularly in situations where continuous monitoring is required. Here are some of the benefits of implementing SHHTs:
- Continuous Monitoring: SHHTs provide a means for continuous monitoring of health parameters, such as vital signs, sleep patterns, and activity levels. This enables caregivers and healthcare professionals to track changes in health status remotely and intervene promptly if necessary.
- Self-Management: SHHTs empower older persons to actively participate in their own care by providing them with real-time feedback and access to health-related information. This promotes self-management and encourages individuals to take control of their well-being.
- Independent Living: SHHTs contribute to maintaining independence by offering support for activities of daily living and ensuring safety within the home environment. Features like fall detection, medication reminders, and home automation systems enhance the quality of life for older adults.
Barriers to SHHT Adoption
While SHHTs offer numerous advantages, there are several barriers that hinder their widespread adoption among older persons. These barriers include:
- Usability: Usability issues pose a significant challenge to the adoption of SHHTs. Older adults may struggle with the complexity of the technology, encounter technical problems, or find the devices obtrusive and disruptive to their daily routines. Enhancements in user interface design and intuitive functionalities can help overcome these challenges.
- Social Acceptance: Social acceptance is another barrier that affects the adoption of SHHTs. Older persons may perceive the technology as difficult to use, worry about disapproval from family members or the public, or find the frequent alerts annoying. Addressing these concerns through education, awareness campaigns, and user-friendly designs can improve social acceptance.
- Cost: Cost and affordability are significant considerations for older persons when it comes to adopting SHHTs. Concerns about the initial purchase cost and ongoing maintenance expenses can deter individuals from embracing these technologies. Strategies to reduce costs and provide financial assistance options can make SHHTs more accessible to a wider range of users.
By understanding the benefits and barriers associated with SHHTs, caregivers and healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about implementing remote monitoring technologies in home care settings. Overcoming the barriers through advancements in usability, addressing social acceptance concerns, and ensuring affordability will pave the way for the wider adoption and utilization of SHHTs in promoting the health and well-being of older adults.
Remote Monitoring Platforms during COVID-19
During the COVID-19 pandemic, remote monitoring platforms (RPM) emerged as potential solutions to reduce the spread of the virus, alleviate congestion in healthcare services, protect health professionals, and maintain the quality and safety of care. These platforms played a crucial role in enabling healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely, ensuring continuous care and support. In this section, we will explore the role of RPM platforms and evaluate the technological platforms used during this challenging time.
Role of RPM Platforms
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) allows healthcare providers to monitor patients outside of traditional care settings using digital medical devices such as weight scales, blood pressure monitors, pulse oximeters, and blood glucose meters. The data collected from these devices are electronically transferred to providers for care management, bringing healthcare into the patient's home [3].
During the COVID-19 public health emergency, telehealth, including RPM, played a vital role in limiting patient exposure by replacing in-person visits with virtual visits. The implementation of RPM increased, with organizations monitoring acute conditions and developing programs to monitor COVID-19 symptoms outside of hospitals. This approach aimed to reduce the burden on hospitals and detect changes in patient status, ensuring timely intervention and care.
Evaluation of Technological Platforms
A study evaluated the capacity and contribution of two different digital platforms in maintaining the quality, safety, and patient engagement in care during the COVID-19 pandemic. The study found positive perceptions regarding the quality and safety of care provided through the platforms.
Participants appreciated the ease of access to health professionals' services and shorter waiting times, which were highly appreciated features of the remote monitoring platforms. However, some encountered challenges such as a lack of training and direct support for users. It is important to address these areas for improvement collaboratively, involving health professionals, patients, health system leaders, decision-makers, and digital platform providers [7].
One of the evaluated platforms, Telecare-Covid, was considered useful and a good response to the needs of patients and healthcare professionals during the health crisis. Many participants suggested that its use should be continued even after the pandemic. However, the lack of training and direct support for users was identified as a common challenge encountered with this platform [7].
As remote monitoring platforms continue to evolve and play an essential role in healthcare, it is crucial to address the identified issues and improve the user experience. Collaborative efforts involving all stakeholders can help enhance the quality, safety, and patient engagement in care provided through these technological platforms.
References
[2]: https://www.healthrecoverysolutions.com/blog/7-common-remote-patient-monitoring-devices
[3]: https://psnet.ahrq.gov/perspective/remote-patient-monitoring
[4]: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10730976/
[5]: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8790688/
[6]: https://bmcgeriatr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12877-024-04702-1