Bariatric Care Facilities And Therapy
Discover top-notch bariatric care facilities for a healthier tomorrow. Expert guidance and cutting-edge procedures await.

Understanding Bariatric Care
When it comes to bariatric care, there are various aspects that contribute to the overall well-being and safety of patients undergoing weight loss surgery. Bariatric nursing plays a vital role in providing specialized care, and accreditation ensures the highest standards of safety in bariatric surgery.
Importance of Bariatric Nursing
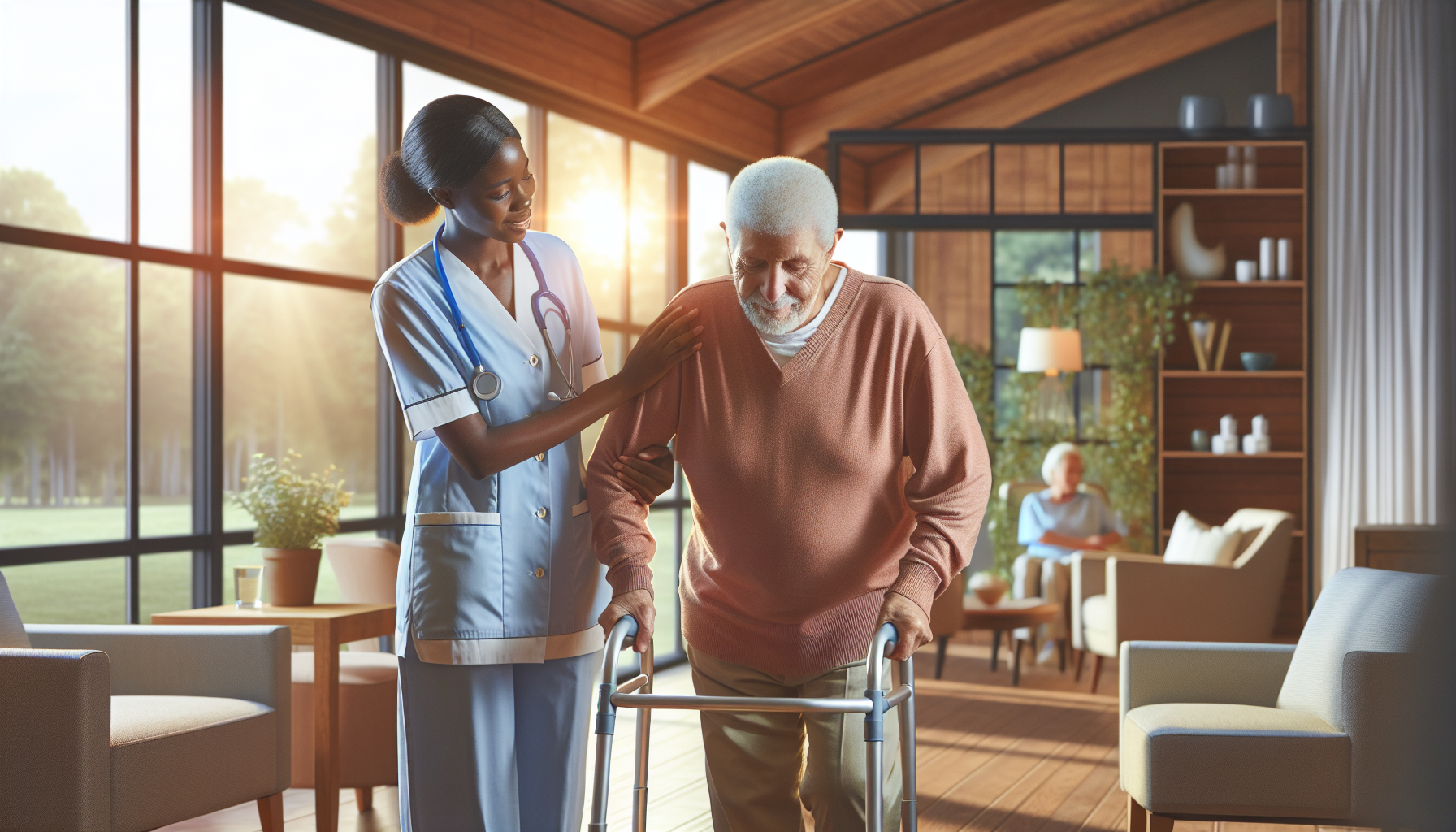
Bariatric nursing is a specialized field that focuses on providing comprehensive care to patients undergoing bariatric surgery. These nurses are equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to address the unique needs of individuals with severe obesity. The Certified Bariatric Nurse (CBN) Program, offered by the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS), aims to assess the professional competence of bariatric nurses and provide them with a premier credential in the field [1].

Certification as a bariatric nurse is highly valued, as it demonstrates a nurse's commitment to delivering high-quality care to severely obese and bariatric surgical patients. Employers and hospital administrators recognize the importance of this certification, as it signifies the nurse's expertise in bariatric care. By obtaining this certification, nurses enhance their knowledge and skills in areas such as patient assessment, preoperative and postoperative care, and long-term management for successful outcomes.
Accreditation and Safety in Bariatric Surgery
Accreditation is an essential aspect of bariatric care facilities and ensures that they meet rigorous standards for safety and quality. Accredited facilities provide a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to bariatric surgery, involving a team of healthcare professionals, including bariatric surgeons, nurses, dietitians, psychologists, and exercise specialists.
Accreditation programs, such as those offered by the ASMBS and other recognized organizations, evaluate the facility's adherence to specific criteria related to patient care, safety protocols, surgical outcomes, and staff qualifications. These programs work to enhance and promote the specialty of bariatric nursing care, ensuring that patients receive the highest level of care throughout their weight loss journey.
By choosing an accredited bariatric care facility, patients can have confidence in the expertise and dedication of the healthcare professionals involved in their care. These facilities follow evidence-based guidelines and best practices to ensure optimal patient outcomes and minimize the risks associated with bariatric surgery.
Understanding the importance of bariatric nursing and seeking care from accredited facilities are key factors in providing safe and effective bariatric care. By prioritizing the specialized knowledge and expertise of bariatric nurses and choosing accredited facilities, patients can embark on their weight loss journey with confidence and support.
Bariatric Surgery Procedures
Bariatric surgery procedures are an important component of bariatric care, aiding in significant weight loss and improving overall health outcomes for individuals struggling with obesity. Here, we will explore three common bariatric surgery procedures: sleeve gastrectomy, gastric bypass, and other common procedures.
Sleeve Gastrectomy
Sleeve gastrectomy (SG) has become one of the most popular bariatric procedures worldwide. In Australia, it accounted for the highest number of bariatric surgeries, with 13,681 cases processed from July 2015 to June 2016. During this procedure, a large portion of the stomach is removed, leaving behind a smaller sleeve-shaped stomach. This reduces the stomach's capacity, leading to early satiety and a decreased appetite. The procedure also removes the part of the stomach that produces the hormone ghrelin, which helps regulate hunger.
Gastric Bypass
Gastric bypass is another commonly performed bariatric surgery procedure. It has shown long-term weight reduction success and numerous health benefits. Studies have reported a mean excess weight loss (EWL) of 56.7% at 10 years or longer post-surgery. During gastric bypass surgery, a small pouch is created at the top of the stomach, and the small intestine is rearranged to connect to this pouch. This restricts food intake and reduces the body's ability to absorb calories and nutrients, resulting in weight loss.
Other Common Procedures
In addition to sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass, there are other common bariatric procedures performed to address obesity. According to a study, nearly all bariatric operations (99.3%) were performed laparoscopically, with gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy being the most frequently performed procedures. Additionally, a combination of gastric restrictive and malabsorptive procedures may be used in some cases. This approach involves creating a small upper gastric pouch and dividing the small intestine to alter the flow of food and digestive juices.
Each bariatric surgery procedure has its own benefits and considerations. The choice of procedure depends on various factors, including the patient's health status, weight loss goals, and the recommendation of the medical team. It is important for individuals considering bariatric surgery to consult with a healthcare professional experienced in bariatric care to determine the most suitable procedure for their unique circumstances.
Patient Care and Education
When it comes to bariatric care, patient care and education play a vital role in ensuring successful outcomes. Preoperative preparation, postoperative lifestyle changes, and patient empowerment are key aspects of comprehensive bariatric care.
Preoperative Preparation
Prior to bariatric surgery, thorough preoperative preparation is essential for both the patient and the healthcare team. This phase involves various assessments, tests, and consultations to determine the patient's suitability for surgery and to ensure they are well-informed about the procedure and its potential risks and benefits.
During the preoperative phase, patients may undergo physical examinations, blood tests, and imaging studies to assess their overall health and identify any potential complications. They may also meet with a registered dietitian to receive dietary guidance and develop a preoperative nutrition plan. Psychological evaluations may be conducted to assess the patient's mental and emotional readiness for surgery.
Education plays a crucial role in preoperative preparation. Patients need to understand the surgical process, the expected outcomes, and the necessary lifestyle changes they will need to make post-surgery. This education empowers patients to set realistic expectations, adhere to guidelines, and make the necessary lifestyle modifications for a successful surgical outcome.
Postoperative Lifestyle Changes
Following bariatric surgery, patients are required to make significant lifestyle changes to support their weight loss and overall well-being. These changes typically include adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and addressing emotional or psychological challenges.
A healthy diet after bariatric surgery focuses on consuming nutrient-dense foods while limiting portion sizes. Patients are advised to follow a specific eating plan, which may involve smaller, more frequent meals and a focus on lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It is important for patients to work closely with a registered dietitian to ensure they are meeting their nutritional needs while maintaining a calorie deficit for weight loss.
Physical activity is also paramount in postoperative care. Regular exercise helps to maintain muscle mass, promote weight loss, and improve overall health. Patients should engage in activities that they enjoy and that are suitable for their physical abilities. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or a certified fitness trainer to develop an exercise plan tailored to individual needs.
Patient Empowerment
Empowering patients is a critical aspect of bariatric care. By providing education, support, and resources, healthcare providers can help patients take an active role in their own care and make informed decisions about their health.
Patient empowerment involves educating patients about their condition, treatment options, and the importance of adhering to recommended guidelines. This education helps patients develop a deeper understanding of their body and the changes they need to make to achieve successful weight loss.
Additionally, support groups and counseling services can provide emotional and psychological support to patients throughout their bariatric journey. These resources create a sense of community and enable patients to share experiences, challenges, and successes with others who have undergone similar procedures.
By emphasizing patient care and education, healthcare providers can support patients in their bariatric surgery journey, help them achieve their weight loss goals, and improve their overall quality of life.
References:
Global Perspective on Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery is a significant component of weight management across the globe. The prevalence of obesity has been rapidly increasing, with the global population facing the consequences of excessive weight gain. Understanding the global perspective on bariatric surgery is crucial in addressing the challenges and opportunities associated with this medical intervention.
Bariatric Surgery Around the World
The prevalence of overweight and obesity has been a growing concern in many parts of the world. In most European countries, 50% of the population is affected by overweight and obesity, with a tripled prevalence since 1980. It is projected that by 2030, 60% of the global population, or 3.3 billion individuals, may suffer from excessive weight gain. This includes 2.2 billion individuals classified as overweight and an additional 1.1 billion individuals classified as obese.
The availability and accessibility of bariatric surgery procedures vary from country to country. In Japan, for instance, only laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) was financially supported by health insurance in 2016. Other bariatric surgery methods were not approved or covered by health insurance, and the criteria for facility approval and patient selection were very strict. Consequently, only twenty facilities were performing bariatric surgery in Japan during that period.
In Singapore, bariatric surgery is supported by government subsidies and compulsory savings in public hospitals. The criteria for eligibility include obese patients with a BMI ≥37.5 kg/m² or a BMI ≥32.5 kg/m² with medical comorbidities of obesity. The supported bariatric surgery procedures in Singapore are laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB), Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), and sleeve gastrectomy (SG).
Australia provides Medicare subsidies for bariatric surgery and postsurgical care in the private sector. However, the rebate is relatively low, resulting in large out-of-pocket expenses for patients. In 2007-2008, only 958 bariatric operations were performed on public patients, while 13,974 surgeries were performed on patients with private health insurance. The most popular bariatric procedure in Australia is sleeve gastrectomy (SG), followed by laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) [2].
Public Health Policies and Support
Public health policies and support play a vital role in the availability and affordability of bariatric surgery worldwide. Countries like Singapore and Australia have implemented policies to subsidize bariatric surgery, making it more accessible to individuals who meet specific criteria.
These policies aim to address the increasing prevalence of obesity and its associated health risks. By providing financial support, governments encourage individuals to seek bariatric surgery as a solution for weight management and potential improvement in comorbidities.
Public health policies also consider the sustainability of bariatric care facilities. Accreditation and safety measures ensure that patients receive high-quality care and minimize the risks associated with surgery.
The global perspective on bariatric surgery highlights the need for continued research, collaboration, and knowledge exchange among countries. Sharing experiences, best practices, and outcomes can contribute to improving patient care and expanding the reach of bariatric surgery as a viable treatment option for obesity.
In the next section, we will explore the challenges and solutions associated with bariatric care facilities, including equipment and facility considerations, as well as staff education and training.
Challenges and Solutions
Providing effective bariatric care requires addressing specific challenges related to equipment and facility considerations, as well as staff education and training. By understanding these challenges and implementing appropriate solutions, bariatric care facilities can ensure the safety and well-being of their patients.
Equipment and Facility Considerations
Patients with obesity face higher risks in hospital settings due to inadequate facility design, equipment, or staff competencies in their care. It is essential for bariatric care facilities to prioritize appropriate equipment and facility considerations to mitigate these risks [7].
To provide safe and effective care, bariatric care facilities should consider the following:
- Bariatric-friendly equipment: Selecting the most appropriate equipment for patients with bariatric care needs is crucial for patient and staff safety. It is recommended to use the same brand or type of bariatric equipment consistently throughout the facility to develop familiarity and skill, reduce delays in patient care, and allow for sharing or moving equipment within the facility.
- Facility design: Facilities should be designed to accommodate the unique needs of patients with obesity. This includes appropriately sized beds, chairs, and bathroom facilities, as well as wider doorways and hallways to ensure ease of movement. Ensuring that the physical environment is accessible and comfortable for patients with obesity promotes their overall well-being and enhances their experience during their stay.
By addressing these equipment and facility considerations, bariatric care facilities can create an environment that promotes safety, comfort, and dignity for patients with obesity.
Staff Education and Training
Ensuring that healthcare staff are properly educated and trained in bariatric care is vital for providing high-quality care and minimizing weight bias and discrimination. Here are key aspects of staff education and training:
- Weight bias and sensitivity training: It is recommended that all staff receive education on the complexity of obesity, weight bias, and weight-based discrimination. Sensitivity training should be provided annually for existing staff and as part of staff orientation for new staff. This training can help eliminate weight bias and discrimination, fostering a supportive and inclusive environment for patients with obesity.
- Procedure-specific training: Anesthesia, operating room staff, and recovery room staff should receive specialized training in bariatric surgical procedures. This ensures that they are familiar with the equipment, instruments, and procedures involved in bariatric care. Expertise in the immediate postoperative care of patients with obesity, including specialized ventilatory support, is crucial for their well-being [5].
By investing in staff education and training, bariatric care facilities can enhance the quality of care provided to patients with obesity and foster a supportive environment that promotes their overall well-being.
Addressing the challenges related to equipment and facility considerations, as well as staff education and training, is essential for bariatric care facilities to provide safe, effective, and compassionate care to their patients with obesity. By implementing appropriate solutions, these facilities can create an environment that supports the unique needs of individuals with obesity and promotes their overall health and well-being.
Long-Term Outcomes and Research
Bariatric surgery has shown promising long-term outcomes in terms of weight loss, diabetes management, and overall improvements in quality of life. Let's explore these aspects in more detail.
Weight Loss and Diabetes Management
Long-term studies have demonstrated significant weight reduction after bariatric surgery. The mean excess weight loss (EWL) at 20 years post-surgery is approximately 48.9%. Gastric bypass procedures have shown even more impressive results, with a mean EWL of 56.7% at 10 years or longer. These findings highlight the effectiveness of bariatric surgery in helping individuals achieve sustained weight loss.
Additionally, bariatric surgery has been associated with improvements in diabetes management. Several studies have shown greater weight loss and remission of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) within the first two years after surgery. Large, long-term observational studies have also demonstrated durable weight loss, diabetes remission, and improvements in lipid profiles even after five years. The Swedish Obese Subjects Study (SOS), which has 15-20 years of follow-up data, reported a 72% remission of T2DM after two years and a 36% remission after ten years post-surgery. These findings highlight the potential of bariatric surgery in managing diabetes in the long term.
Quality of Life Improvements
Bariatric surgery has been found to significantly improve the quality of life (QoL) of individuals undergoing the procedure. Studies have shown that bariatric surgery leads to greater improvements in QoL compared to other obesity therapies. Physical quality of life tends to improve faster than mental quality of life, with noticeable improvements occurring within the first two years after surgery. These improvements in QoL can have a positive impact on various aspects of an individual's life, including physical functioning, psychological well-being, and social interactions.
Ongoing Studies and Predictions
While the long-term outcomes of bariatric surgery have been promising, there are still areas that require further research. Ongoing studies aim to identify predictors of outcomes, long-term complications, survival rates, and the impact of bariatric surgery on micro- and macrovascular events, mental health outcomes, and costs.
It's worth noting that bariatric surgery has been associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, heart failure, myocardial infarction, and stroke [3]. A study in Utah comparing the long-term survival of individuals who underwent bariatric surgery with weight-matched controls found a 40% reduction in all-cause mortality after seven years, along with reductions in cardiovascular and diabetes-related mortality. These findings highlight the potential long-term health benefits of bariatric surgery.
As research continues to unfold, it is expected that more insights will be gained regarding the long-term outcomes of bariatric surgery, contributing to improved patient care and better understanding of its overall impact on health and well-being.
In summary, bariatric surgery has shown promising long-term outcomes in terms of weight loss, diabetes management, and quality of life improvements. While further research is needed to fully understand all aspects of bariatric surgery, the existing evidence highlights its potential to positively impact the lives of individuals seeking long-term solutions for weight management and associated health conditions.
References
[1]: https://asmbs.org/professional-education/cbn/
[2]: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6484931/
[3]: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10353499/
[4]: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11695-018-3593-1
[5]: https://www.facs.org/about-acs/statements/recommendations-for-facilities-performing-bariatric-surgery/
[6]: https://peakbariatric.com/bariatric-qualifications-certifications/
[7]: https://obesitycanada.ca/resources/bariatric-friendly/