The Most Common Mental Illness In The Elderly
Discover the most common mental illness in the elderly. Learn about depression, anxiety, dementia, and more. Support mental well-being today!

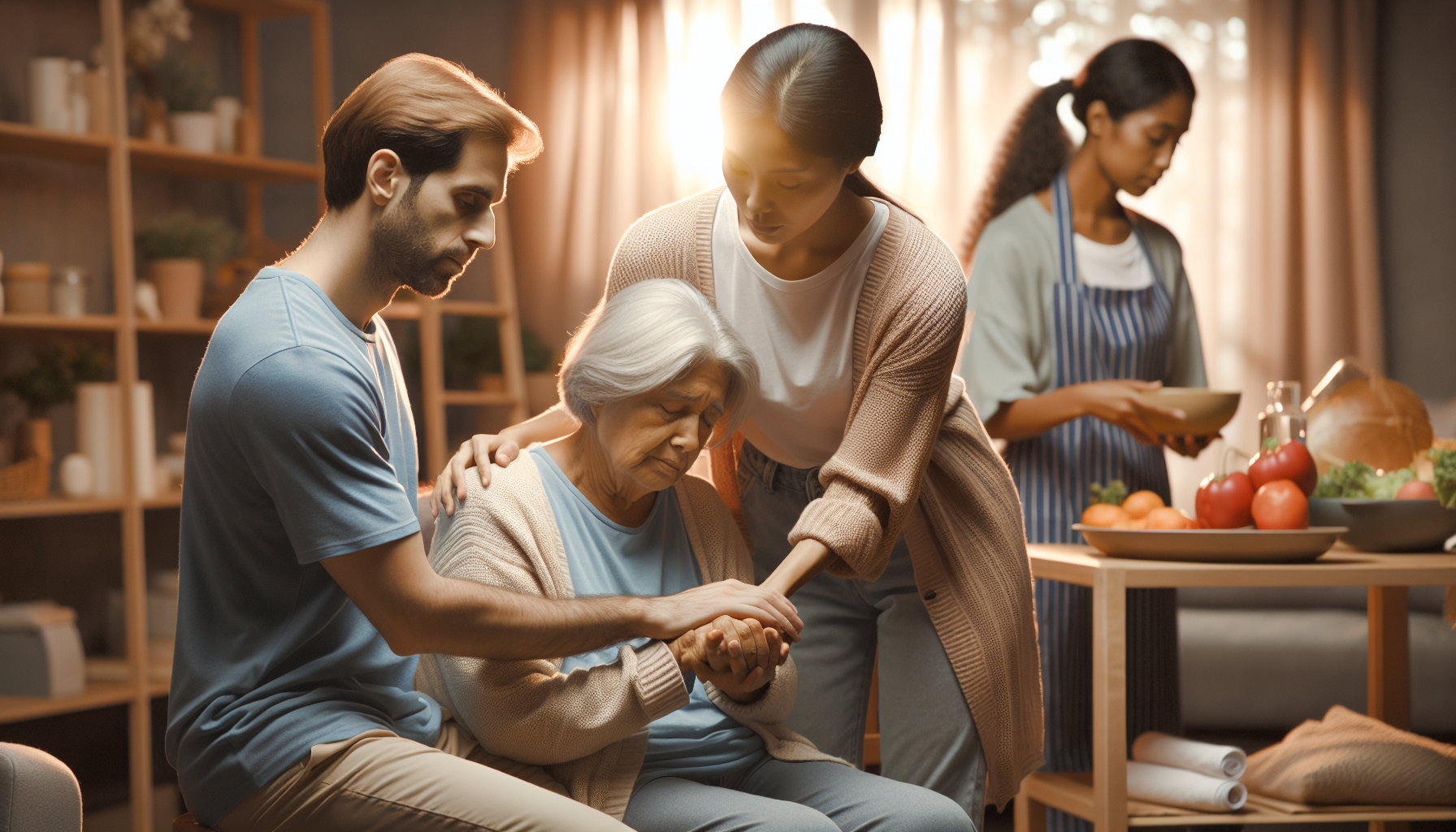
Understanding Mental Health in the Elderly
In order to provide appropriate care and support for the elderly, it's important to have a comprehensive understanding of mental health conditions that may affect them. This section explores the common mental health conditions in the elderly and provides insights into the prevalence of mental disorders among older adults.
Common Mental Health Conditions
Depression, anxiety disorders, dementia, substance abuse, and suicide risk are among the most common mental health conditions that affect the elderly population. These conditions can have a significant impact on the well-being and quality of life of older adults.

Depression stands out as the most common mental health problem for older adults. It affects around 7% of the elderly population worldwide, according to the World Health Organization. In the United States, about 15 out of 100 adults over the age of 65 experience depression. Depression can lead to other medical illnesses, worsen functioning, and decrease the overall quality of life for older adults.
Anxiety disorders are also prevalent among the elderly, although they often go unrecognized or mistaken for other issues related to aging. Approximately 2% of older adults globally experience anxiety disorders [1].
Dementia, a condition characterized by cognitive decline, memory loss, and impaired thinking abilities, is another common mental health issue in the elderly population. It affects approximately 5% of older adults globally. Mental health challenges can also arise in individuals with dementia, exacerbating the overall complexity of care.
Substance abuse, though often overlooked, can occur in older adults. The prevalence of substance abuse among the elderly is a concern, particularly when it co-occurs with other mental health conditions.
Suicide risk is another critical aspect of mental health in the elderly. Older adults, especially older white men, are at higher risk for suicide. It is important to be vigilant and provide appropriate support to prevent and address suicide risk in this vulnerable population.
Prevalence of Mental Disorders in Older Adults
The prevalence of mental health disorders in older adults is significant, with about 15% of adults aged 60 and over experiencing a mental disorder in developed countries [1]. However, it's important to note that the actual prevalence may be underestimated due to factors such as stigma, lack of awareness, underdiagnosis, and inadequate treatment of these conditions.
Mental health conditions in older individuals are often comorbid with other health conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes, and musculoskeletal problems, which can complicate overall health management. The presence of these comorbidities emphasizes the need for integrated and holistic approaches to address mental health concerns in the elderly population.
By understanding the common mental health conditions and the prevalence of mental disorders among older adults, caregivers can better recognize and provide appropriate support for the mental well-being of the elderly. It is crucial to prioritize mental health care alongside physical health care to enhance the overall quality of life for older individuals.
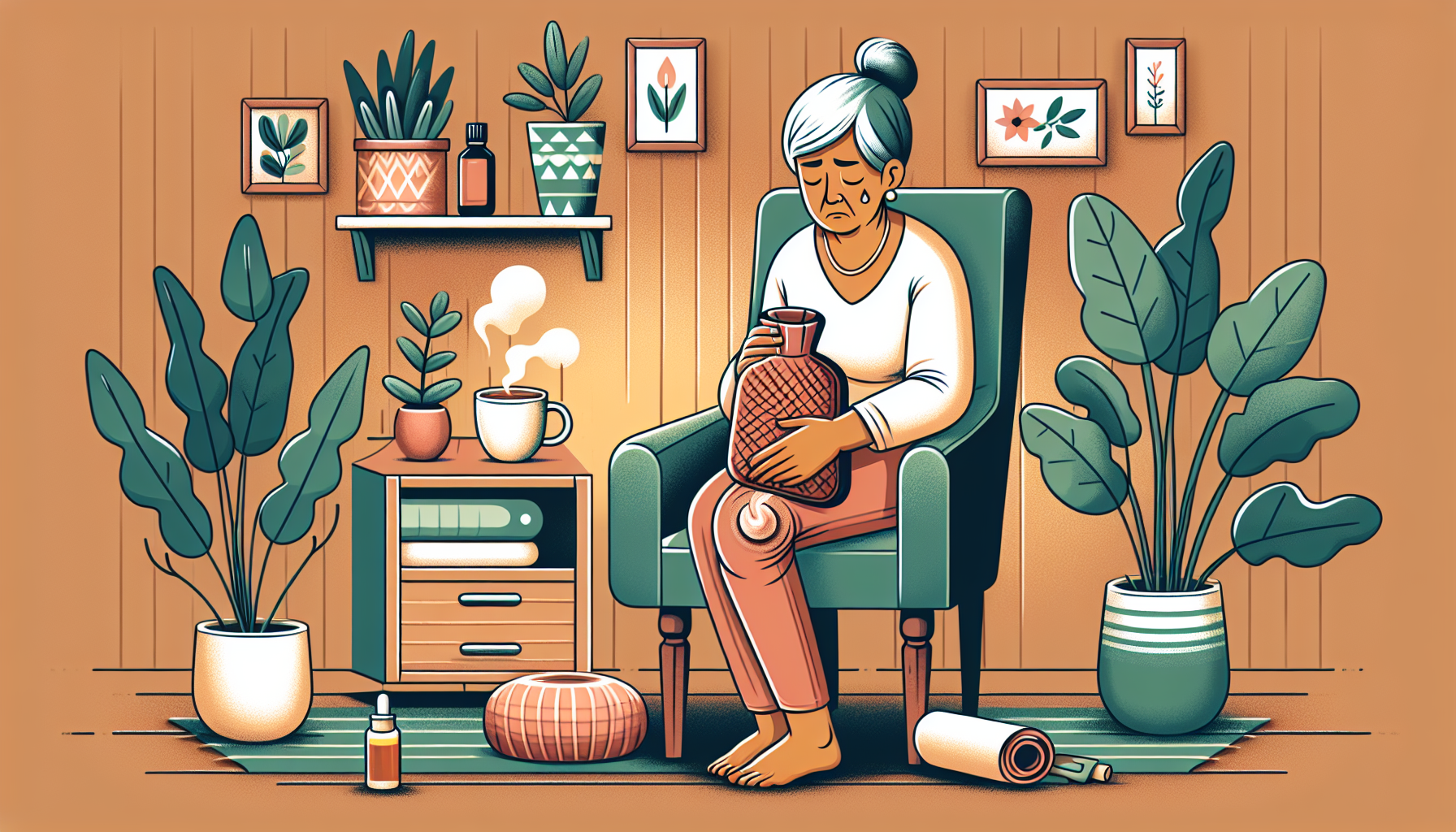
Depression in the Elderly
Depression is the most common mental disorder in the elderly, affecting a significant portion of the elderly population worldwide. It is estimated that around 7% of older adults experience depression. In the United States, depression affects approximately 15 out of 100 adults over the age of 65. This mental health condition can have a profound impact on the overall well-being and quality of life of older adults.
The Impact of Depression
Depression in the elderly can manifest in various ways and have a significant impact on their physical health, cognitive function, and social interactions. Some common symptoms include persistent sadness, loss of interest or pleasure in activities, changes in appetite, sleep disturbances, fatigue, and feelings of worthlessness or guilt. If left untreated, depression can worsen chronic health conditions, impair cognitive function, and increase the risk of suicide.
It is important to note that while it is common for older adults to experience challenges and losses as they age, clinical depression is not a normal part of aging [3]. Depression is a treatable condition, and seeking appropriate help and support is essential.
Risk Factors for Depression
Several factors contribute to the development of depression in older adults. These can include:
Understanding the risk factors can help identify older adults who may be at a higher risk of developing depression and enable timely intervention.
Treatment Options for Depression
Fortunately, depression is treatable, and there are various options available for managing and alleviating symptoms in older adults. Treatment approaches for depression in the elderly may include:
Remember, seeking help and treatment is essential for individuals experiencing depression. With appropriate support and intervention, older adults can find relief and improve their overall mental health, leading to enhanced quality of life.
Anxiety Disorders in the Elderly
Anxiety disorders are a common mental health concern among older adults, often being mistaken for physical, cognitive, or emotional issues that occur with aging. Approximately 15% of older adults suffer from anxiety disorders, making it a significant issue in this population. Let's explore the types of anxiety disorders, recognizing and managing anxiety, as well as treatment options available for older adults.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders encompass a range of conditions that can significantly impact the mental well-being of older adults. Some common types of anxiety disorders include:
These anxiety disorders can often coexist with depression and other mental health conditions in older adults.
Recognizing and Managing Anxiety
Recognizing anxiety in older adults can be challenging, as symptoms may be mistaken for other age-related issues. Common signs of anxiety in older adults may include excessive worry, restlessness, irritability, sleep disturbances, and physical symptoms like muscle tension or a rapid heartbeat. Caregivers and healthcare professionals should be vigilant in identifying these signs and providing appropriate support.
Managing anxiety in older adults involves a combination of strategies including:
Treatment Options for Anxiety
Treatment options for anxiety disorders in older adults may vary depending on the severity and individual needs. Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and problem-solving therapy (PST), has shown promising results in reducing the incidence of depressive and anxiety disorders in older adults. These therapeutic approaches focus on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and developing coping strategies.
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage anxiety symptoms. However, medication should always be carefully evaluated and monitored by a healthcare professional to ensure proper dosage and minimize potential side effects.
It's important for caregivers and healthcare providers to work collaboratively with older adults to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and preferences. By providing appropriate support, understanding, and effective treatment, it is possible to help older adults manage their anxiety and improve their overall mental well-being.
Dementia and Mental Health
Dementia is a critical mental health issue that affects a significant number of elderly individuals. It is estimated to impact around 5 to 8 percent of people aged 65 and older. Understanding the link between dementia and mental health is crucial for providing appropriate support and care to individuals facing these challenges.
Link Between Dementia and Mental Health
Dementia is characterized by a decline in cognitive abilities, memory loss, and changes in behavior and personality. It can have a profound impact on an individual's mental well-being. According to the National Institute on Aging (NIH), depression is common in people with Alzheimer's and related dementias. Additionally, there may be an increased risk of suicide attempts in individuals recently diagnosed with dementia. Research is still ongoing to determine effective treatment options for depression in people with dementia.
Challenges of Mental Health in Dementia
Mental health challenges in individuals with dementia can be complex and multifaceted. The cognitive decline and memory loss associated with dementia can contribute to feelings of confusion, frustration, and anxiety. Changes in behavior and difficulty in expressing oneself may lead to social isolation and a decreased quality of life. Caregivers and family members play a crucial role in recognizing and addressing these challenges and providing the necessary support.
Support for Individuals with Dementia
Supporting individuals with dementia requires a comprehensive approach that addresses their mental health needs. Creating a supportive and stimulating environment can help promote overall well-being. Providing social engagement, meaningful activities, and cognitive stimulation can help improve mood and reduce feelings of isolation.
In addition to environmental support, there are various interventions and treatments available to assist individuals with dementia. These may include medication, cognitive therapy, and behavioral interventions tailored to the specific needs of the individual. Support groups and counseling can also be beneficial for both individuals with dementia and their caregivers, providing a space to share experiences and receive emotional support.
It is essential for caregivers and healthcare professionals to work together to develop personalized care plans that take into consideration the unique challenges associated with dementia and mental health. By prioritizing mental health support, we can enhance the well-being and quality of life for individuals living with dementia.
Substance Abuse in the Elderly
Substance abuse is a significant mental health issue that is often overlooked in the elderly population. It is estimated that approximately 17% of adults aged 60 and older struggle with alcohol abuse or misuse, highlighting the importance of addressing substance abuse in this age group.
Prevalence of Substance Abuse
The prevalence of substance abuse in the elderly is a cause for concern. Substance abuse can include alcohol, prescription drugs, or illicit substances. Research suggests that older adults may turn to substances as a way to cope with physical or emotional pain, loneliness, or as a means of self-medication.
Recognizing and Addressing Substance Abuse
Recognizing substance abuse in the elderly can be challenging due to various factors, including denial, stigma, and the tendency to attribute symptoms to aging or other health conditions. However, there are signs that caregivers and healthcare professionals can look out for, such as changes in behavior, unexplained injuries, neglecting personal hygiene, or social withdrawal.
Addressing substance abuse in the elderly requires a multi-faceted approach. It is crucial to create a supportive and non-judgmental environment where individuals feel comfortable discussing their struggles. Encouraging open communication and providing education about the risks and consequences of substance abuse can help raise awareness and promote early intervention.
Treatment Options for Substance Abuse
Treating substance abuse in the elderly often involves a combination of approaches tailored to the individual's needs. Treatment options may include:
It is important to approach substance abuse treatment in the elderly holistically, taking into account their physical and mental health, as well as any social or environmental factors that may contribute to their substance abuse. Collaborating with healthcare professionals and seeking specialized addiction services can greatly increase the chances of successful recovery and improved overall well-being.
By recognizing the prevalence of substance abuse in the elderly, understanding the signs and symptoms, and providing appropriate treatment and support, caregivers and healthcare professionals can make a positive impact on the lives of older adults struggling with substance abuse.
Suicide Risk in the Elderly
The issue of suicide risk among the elderly is a concerning and complex area of mental health. Understanding the factors that contribute to suicide risk, recognizing warning signs, and implementing effective prevention strategies are essential in providing support and care for older adults. In this section, we will explore the understanding of suicide risk, warning signs and prevention, as well as the support available for suicide prevention in the elderly.
Understanding Suicide Risk
Suicide rates are alarmingly high among older adults, particularly among elderly white men. In fact, older white men account for 37% of all suicides in that age group. This demographic faces unique challenges that contribute to an increased risk of suicide. Loneliness, social isolation, chronic medical conditions, limited access to healthcare, and the loss of loved ones are some of the factors that can contribute to suicidal ideation and behavior.
It's important to recognize that suicidal thoughts and behaviors in the elderly are often associated with underlying mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, or substance abuse. Identifying these conditions and providing appropriate treatment and support are crucial steps in addressing suicide risk.
Warning Signs and Prevention
Recognizing the warning signs of suicide in the elderly is vital for early intervention and prevention. Some common indicators include expressing feelings of hopelessness, talking about death or suicide, withdrawing from social activities, giving away possessions, and significant changes in mood or behavior. It's important to take these signs seriously and seek professional help immediately.
Preventing suicide in the elderly requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes raising awareness, reducing stigma around mental health, promoting social connections, and providing accessible mental health services. Educating caregivers, family members, and healthcare professionals about the risk factors and warning signs of suicide is crucial for early intervention. Additionally, implementing screening programs and ensuring appropriate mental health support and resources are available can help prevent suicide among older adults.
Support for Suicide Prevention
Various organizations and resources are available to support suicide prevention in the elderly. National helplines, such as the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline (1-800-273-TALK), provide immediate support and guidance to individuals in crisis. Local mental health clinics, community centers, and senior centers may also offer counseling services and support groups specifically tailored to the needs of older adults.
In addition to professional support, involving family members, friends, and caregivers in the care and well-being of older adults can be instrumental in suicide prevention. Encouraging open communication, fostering social connections, and ensuring a supportive environment can significantly reduce suicide risk.
By understanding the risk factors, recognizing warning signs, and implementing effective prevention strategies, we can make a difference in the lives of older adults at risk of suicide. It is essential to prioritize mental health, promote social connectedness, and ensure accessible mental health resources for older adults to prevent suicide and provide them with the support and care they need.
Promoting Mental Well-being in the Elderly
Taking proactive steps to promote mental well-being can significantly contribute to the overall mental health of older adults. Prevention strategies, psychotherapy and counseling, and psychosocial and exercise interventions play crucial roles in maintaining and enhancing mental well-being in the elderly.
Prevention Strategies for Mental Disorders
Prevention efforts should be focused on preventing mental disorders in older adults rather than solely focusing on sickness and treatment. Research has shown that existing prevention programs can reduce the incidence of new disorders and prevent the recurrence of depression and anxiety.
Implementing prevention strategies involves identifying and addressing risk factors such as social isolation, chronic health conditions, and life transitions. Promoting social engagement, providing education and support, and encouraging healthy lifestyle choices can all contribute to preventing the onset of mental disorders.
Role of Psychotherapy and Counseling
Psychotherapy and counseling have proven to be effective in reducing the incidence of depressive and anxiety disorders in older adults. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and problem-solving therapy (PST) have shown promising results in improving mental well-being and preventing the onset of mental disorders.
These therapeutic approaches help individuals develop coping mechanisms, challenge negative patterns of thinking, and enhance problem-solving skills. By addressing underlying issues and providing support, psychotherapy and counseling contribute to maintaining mental well-being and preventing the development of mental disorders.
Benefits of Psychosocial and Exercise Interventions
Psychosocial and exercise interventions have the potential to address specific risk factors and promote mental health in older adults. Programs such as reminiscence therapy, which encourages individuals to reflect on positive life experiences, have shown promising results in reducing depressive symptoms.
Exercise interventions, including aerobic exercise and strength training, have also been associated with improved mental well-being in older adults. Regular physical activity can help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety and enhance overall cognitive function.
By incorporating psychosocial and exercise interventions into the daily routine of older adults, caregivers can contribute to their mental well-being and create a supportive environment that promotes overall mental health.
Promoting mental well-being in the elderly is a multifaceted approach that encompasses prevention strategies, psychotherapy and counseling, and psychosocial and exercise interventions. By taking proactive steps to address risk factors and provide support, caregivers can play a vital role in maintaining and enhancing the mental well-being of older adults.
References
[2]:
[3]:
[4]:
[5]:
[6]: