Potential Benefits of Nutrition Supplements for Elderly
Unlock the potential benefits of nutrition supplements for the elderly. Enhance their health and well-being with expert guidance!
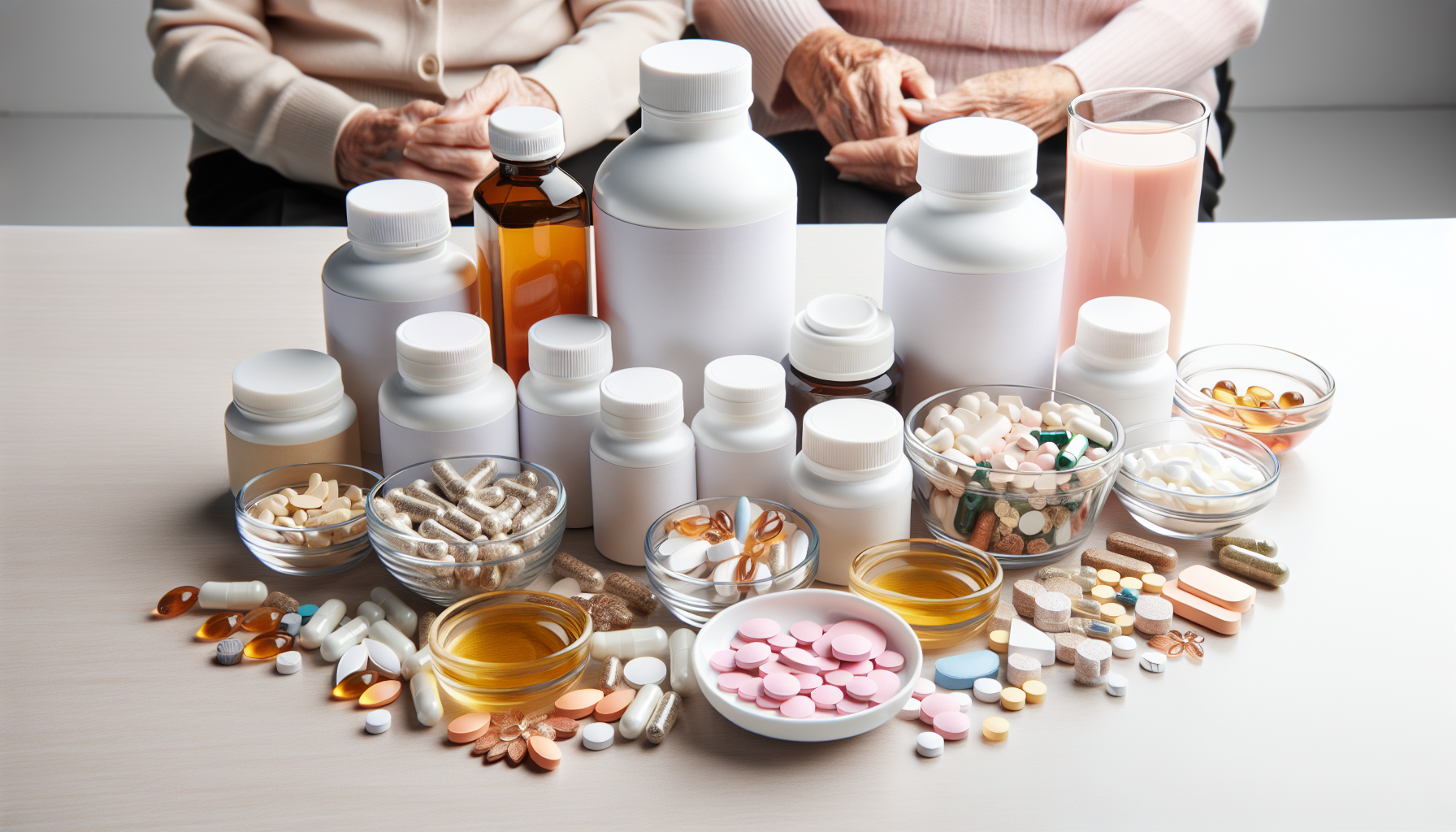

The Importance of Nutrition for the Elderly
As individuals age, proper nutrition becomes increasingly important for maintaining good health and overall well-being. The nutritional needs of the elderly are unique and must be carefully addressed to support their physical and cognitive health. Several factors can affect the nutritional status of older adults, making it essential to prioritize their dietary needs.
Nutritional Needs of the Elderly
Older adults are at an increased risk for malnutrition due to various factors, including reduced food intake, decreased absorption of nutrients, and increased nutrient needs. Aging is associated with physiological changes that can affect appetite, digestion, and nutrient absorption. As a result, the elderly may require a more nutrient-dense diet to meet their nutritional needs and maintain optimal health.
It is important for older adults to focus on consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of foods from different food groups. This helps ensure an adequate intake of essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, protein, and fiber. Nutrients like vitamin D, vitamin B12, calcium, and magnesium are particularly important for the elderly and play crucial roles in maintaining bone health, cognitive function, and overall well-being.

Factors Affecting Nutritional Status
Numerous factors can influence the nutritional status of older adults. Reduced physical activity, changes in taste and smell perception, hormonal alterations, gastrointestinal changes, oral health issues, and psychological factors like depression and social isolation can all contribute to decreased food intake and nutrient deficiencies among the elderly population [2]. Additionally, the presence of age-related chronic diseases like type II diabetes, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, and malnutrition can further exacerbate nutrient deficiencies among older adults.
To address these challenges and promote optimal nutrition, it is crucial to provide older adults with appropriate dietary guidance and support. Encouraging regular physical activity, improving access to nutritious foods, addressing sensory impairments, and addressing psychological well-being can all contribute to improving the nutritional status of the elderly population.
By understanding the nutritional needs of the elderly and the factors that can impact their nutritional status, caregivers and families can take proactive steps to ensure that older adults receive the necessary nutrients for healthy aging. A balanced and nutrient-rich diet is key to supporting their overall health and well-being.
Common Nutrient Deficiencies in the Elderly
As individuals age, their nutritional needs may change, and they become more susceptible to certain nutrient deficiencies. Understanding these common deficiencies is crucial for maintaining the health and well-being of the elderly population. Here are four key nutrient deficiencies that are frequently observed in older adults: vitamin D, vitamin B12, calcium, and magnesium.
Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency is especially prevalent among older adults. This deficiency can arise due to reduced sun exposure, decreased skin synthesis of vitamin D, and a decline in the efficiency of vitamin D absorption. Vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health and supporting the immune system. Inadequate levels of vitamin D can lead to an increased risk of falls, fractures, and weakened immune function.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Another common nutrient deficiency in the elderly is vitamin B12. Older adults often experience a decrease in the body's ability to absorb vitamin B12 efficiently. Vitamin B12 is essential for nerve function, DNA synthesis, and the production of red blood cells. Insufficient levels of this vitamin can result in anemia, fatigue, memory problems, and neurological issues.
Calcium Deficiency
Calcium is crucial for maintaining strong bones and teeth. However, many older adults do not consume enough calcium-rich foods or have reduced calcium absorption. Inadequate calcium intake can lead to decreased bone density, increased risk of fractures, and osteoporosis. It is worth noting that vitamin D is necessary for calcium absorption, so deficiencies in both nutrients often coexist.
Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium is involved in various physiological processes, including bone health, muscle function, and energy production. Older adults may experience reduced magnesium absorption due to aging and various medications. Magnesium deficiency can contribute to muscle cramps, weakness, sleep disturbances, and increased risk of cardiovascular diseases.
To address these nutrient deficiencies, it is essential to incorporate nutrient-rich foods into the diet and consider dietary supplements, under the guidance of a healthcare professional. By ensuring adequate intake of these vital nutrients, caregivers and families can help support the overall health and well-being of older adults.
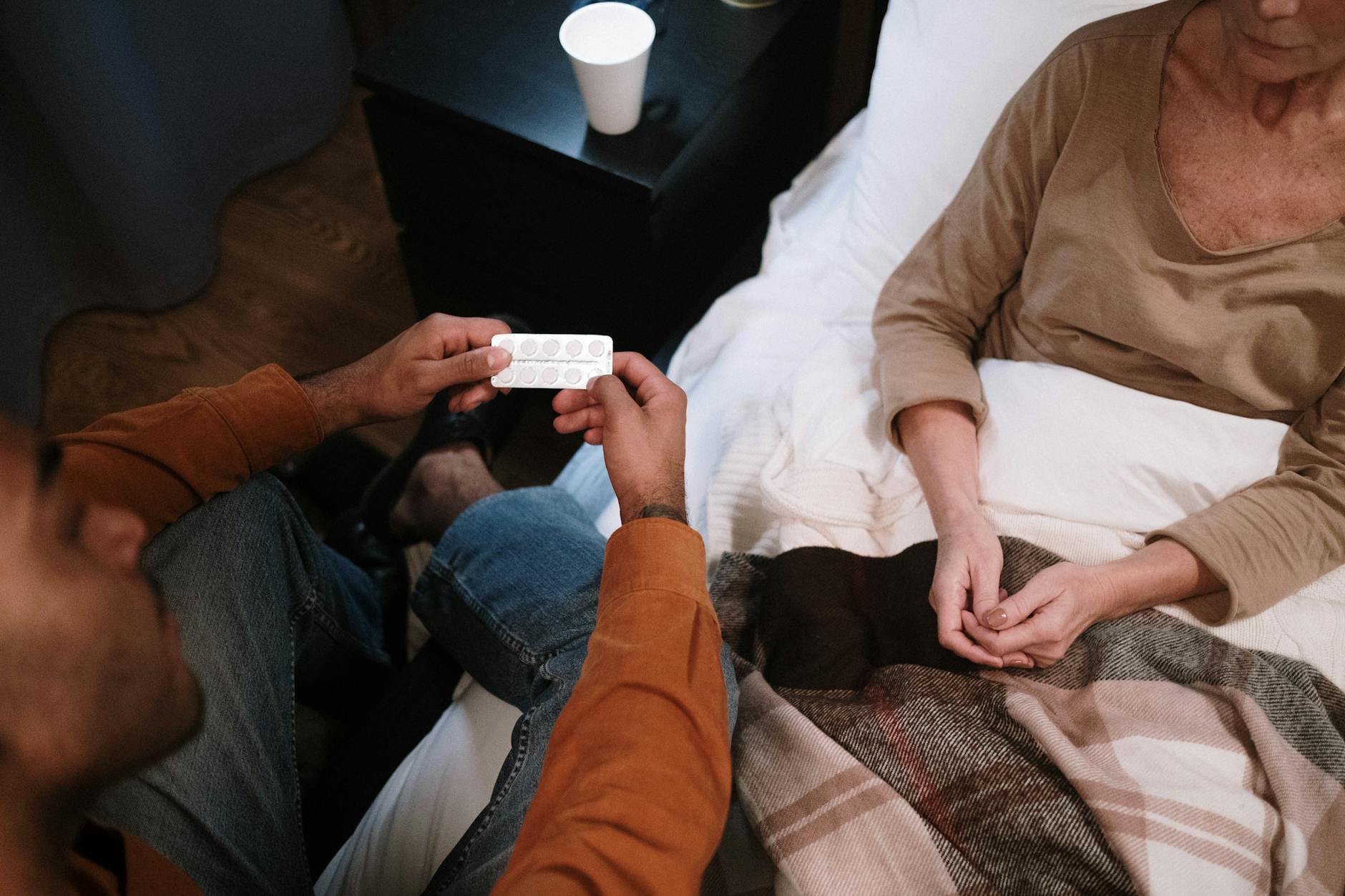
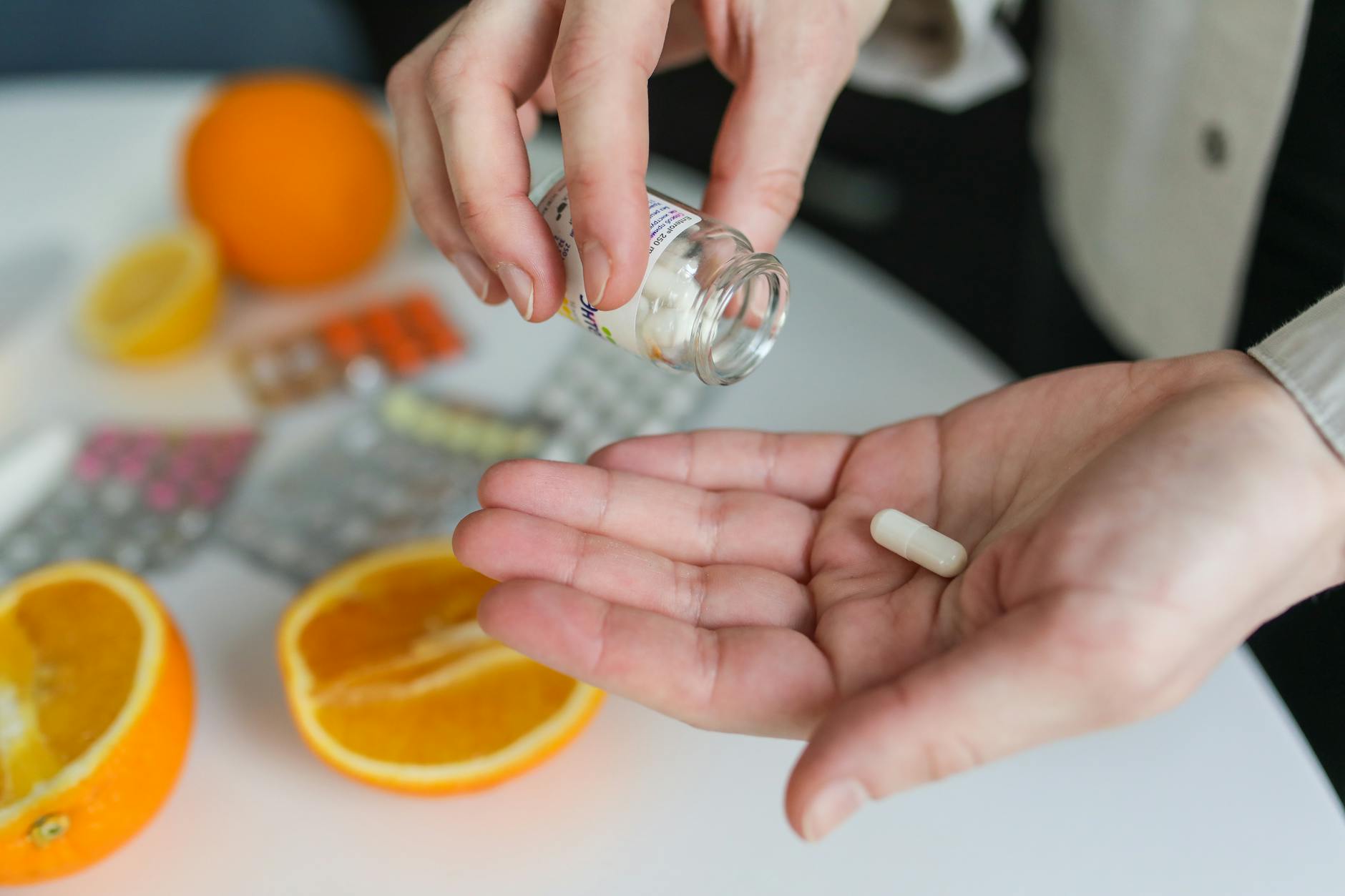
Dietary Supplements for the Elderly
When it comes to meeting the nutritional needs of the elderly, dietary supplements can play a significant role. Supplements can provide essential vitamins and minerals that may be lacking in the diet, helping to support overall health and wellbeing. In this section, we will explore two types of dietary supplements commonly used by the elderly: multivitamin-mineral supplements and individual nutrient supplements.
Multivitamin-Mineral Supplements
Multivitamin-mineral supplements are a convenient option for older adults to ensure they are meeting their nutrient needs. These supplements typically contain a combination of essential vitamins and minerals in one tablet or capsule. By taking a daily multivitamin-mineral supplement, the elderly can supplement any potential deficiencies and support their overall health.
It's important to note that while multivitamin-mineral supplements can be beneficial, they are not a substitute for a balanced diet. These supplements should complement a healthy eating plan rather than replace the consumption of nutrient-rich foods. It's always best to obtain as many nutrients as possible from whole foods to ensure a wide range of beneficial compounds.
Individual Nutrient Supplements
In addition to multivitamin-mineral supplements, older adults may benefit from individual nutrient supplements targeting specific deficiencies. Certain vitamins and minerals are commonly lacking in the diets of the elderly, and supplementation can help bridge these gaps. However, it is crucial to seek professional guidance before starting any individual nutrient supplements.
Consulting a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian can help identify specific nutrient deficiencies and recommend appropriate supplements. Some common individual nutrient supplements for the elderly include:
Remember, it's important to choose reputable brands and high-quality supplements when considering individual nutrient supplements. Look for third-party testing for safety and quality assurance. Additionally, be cautious about supplements with additives, fillers, and artificial ingredients. Always follow the directions provided and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new dietary supplement.
While dietary supplements can be beneficial for the elderly, it's important to remember that they should not replace a balanced diet. Nutrients obtained from whole foods are generally more bioavailable and come with additional health benefits. Supplements should be considered in the context of an individual's diet and lifestyle, with guidance from a healthcare provider or dietitian.
Considerations for Choosing Supplements
When it comes to choosing nutrition supplements for the elderly, there are several important considerations to keep in mind. These considerations can help ensure that the supplements selected are safe, effective, and suitable for the specific needs of the elderly individual.
Professional Guidance
Seeking professional guidance is crucial when choosing dietary supplements for the elderly. Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or registered dietitian, can provide valuable insight into the specific nutritional needs of the individual and help determine if supplements are necessary. They can also provide recommendations on the appropriate dosage and potential interactions with medications. Professional guidance is particularly important for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking multiple medications to ensure that the supplements do not interfere with their health or prescribed treatments.
Quality and Safety
Ensuring the quality and safety of supplements is of utmost importance. When choosing supplements, it is advisable to opt for reputable brands that follow good manufacturing practices. Look for supplements that have undergone third-party testing for safety and quality assurance. This can help ensure that the product contains the stated ingredients in the correct amounts and is free from contaminants or impurities. It is important to note that dietary supplements are not regulated by the FDA for safety or efficacy, so selecting high-quality products is essential.
Additives and Artificial Ingredients
Another consideration when choosing supplements for the elderly is to carefully examine the ingredient list. It is advisable to avoid supplements that contain excessive additives, fillers, or artificial ingredients. Some supplements may contain unnecessary ingredients that can potentially cause adverse effects or allergic reactions. Opting for supplements with minimal additional ingredients can help reduce the risk of complications and ensure that the focus remains on the necessary nutrients. It is important to read labels and choose products that contain the required vitamins or minerals without unnecessary additives [6].
By taking these considerations into account, caregivers and families of the elderly can make informed decisions when selecting nutrition supplements. Professional guidance, quality assurance, and attention to ingredients can help ensure that the chosen supplements are safe, effective, and beneficial for the specific nutritional needs of the elderly individual. Remember, it is always advisable to consult with healthcare professionals before starting any new supplements to ensure the best possible outcomes for the elderly individual's health and well-being.
Managing Nutritional Needs in the Elderly
As individuals age, it becomes increasingly important to manage their nutritional needs to support their overall health and well-being. This section will explore some key aspects of managing nutritional needs in the elderly, including balanced diet recommendations, sodium intake and heart health, and the importance of evaluation and individualized recommendations.
Balanced Diet Recommendations
One of the foundations for managing nutritional needs in the elderly is maintaining a balanced diet. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025 recommend specific intake levels for certain vitamins and minerals for individuals over the age of 50. For example, it is recommended that women over the age of 50 consume 1,200 mg of calcium per day and individuals age 51 to 70 consume 600 IU of vitamin D, while those over 70 should aim for 800 IU of vitamin D. Additionally, vitamin B12 is recommended at 2.4 mcg per day for individuals over age 50.
While it is ideal to obtain most vitamins and minerals from food sources, dietary supplements may be considered in the context of an individual's diet and lifestyle, with guidance from a healthcare provider or dietitian [5]. A balanced diet should include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats to ensure a well-rounded nutritional intake.
Sodium Intake and Heart Health
Monitoring sodium intake is particularly important for managing nutritional needs in the elderly, as excessive sodium consumption can contribute to heart health issues. High sodium intake has been linked to increased blood pressure, which can raise the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions.
To manage sodium intake, it is recommended to limit the use of table salt and processed foods, which often contain high amounts of sodium. Instead, opt for fresh, whole foods and use herbs and spices to add flavor to meals. By reducing sodium intake, individuals can support their heart health and overall well-being.
Evaluation and Individualized Recommendations
Managing nutritional needs in the elderly requires a personalized approach. Each individual has unique dietary requirements, health conditions, and lifestyle factors that should be taken into consideration. It is recommended to consult with healthcare providers, such as doctors or dietitians, who can evaluate an individual's nutritional status and provide tailored recommendations.
Healthcare professionals can assess an individual's overall health, current medications, and any specific nutrient deficiencies or excesses that need to be addressed. They can also provide guidance on dietary modifications, including the use of dietary supplements, if necessary. This personalized approach ensures that nutritional needs are met in a safe and effective manner.
It's important to note that dietary supplements, including vitamins and minerals, should be approached with caution. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not have authority over dietary supplements, and their safety and efficacy may vary. It is crucial to consult with healthcare providers and consider the potential risks associated with dietary supplements before incorporating them into an individual's regimen.
By following balanced diet recommendations, monitoring sodium intake, and seeking individualized recommendations, caregivers and families can effectively manage the nutritional needs of the elderly, promoting their overall health and well-being.
References
[2]:
[3]:
[4]:
[5]:
[6]: