Left Side Stroke Recovery Exercises For Seniors
Discover effective left side stroke recovery exercises for seniors. Regain strength, mobility, and independence with targeted exercises.

Stroke Recovery Exercises Overview
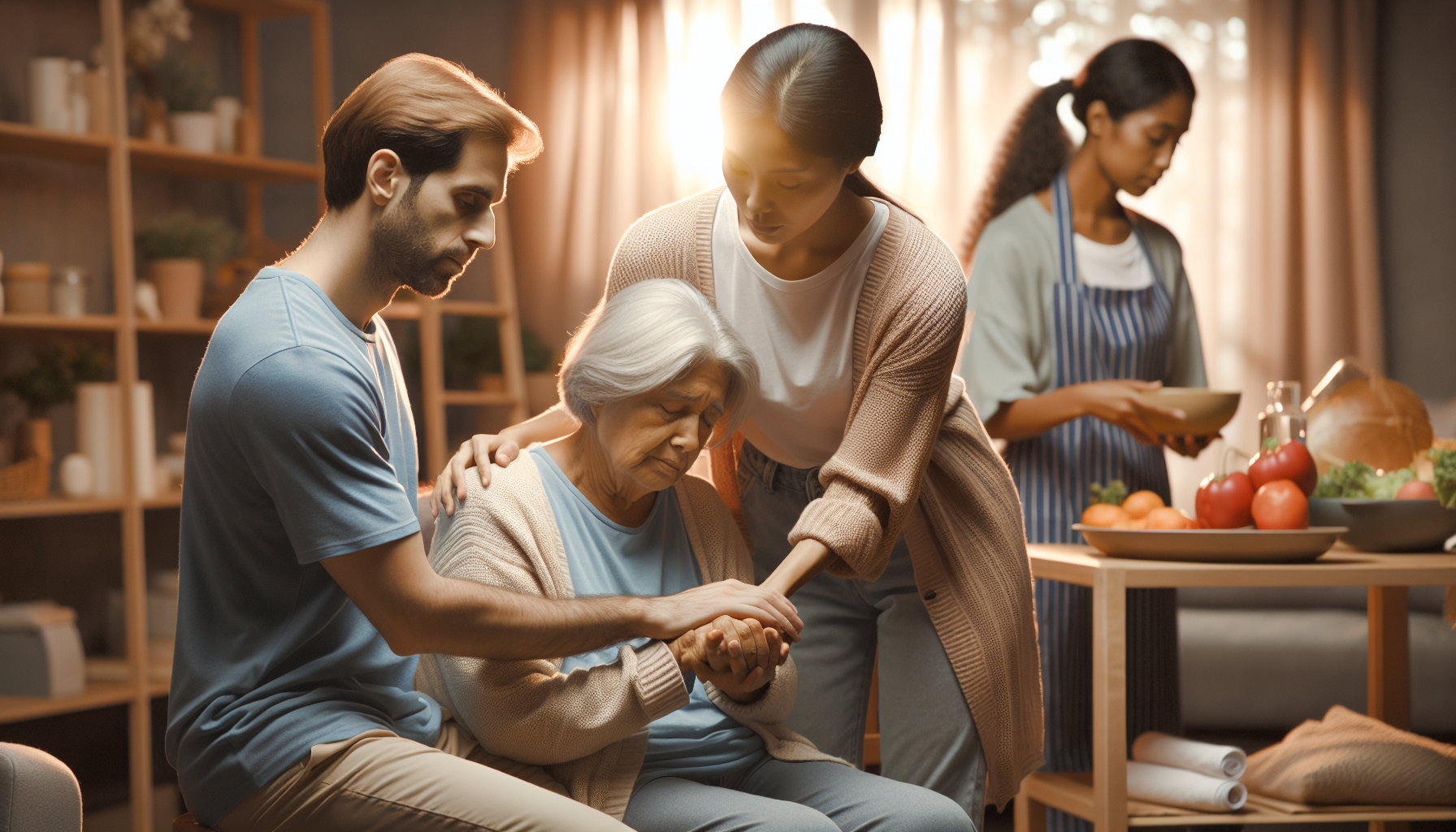
When it comes to stroke recovery, exercise plays a crucial role in promoting physical and cognitive rehabilitation. Engaging in appropriate exercises after a left-side stroke can help seniors regain strength, improve mobility, and enhance overall quality of life. In this section, we will explore the importance of exercise after a stroke and provide safe exercise guidelines.
Importance of Exercise After Stroke
Physical activity after stroke is essential for various reasons. It helps to preserve muscle strength, assists with balance and walking, and enhances energy levels, thereby improving the ability to carry out daily activities [1]. Regular exercise also contributes to cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of future strokes.

In addition to physical benefits, exercise can have a positive impact on mental and emotional well-being. It can help reduce feelings of depression and anxiety often experienced after a stroke. By engaging in exercise, seniors can regain confidence, regain their independence, and enhance their overall quality of life.
Safe Exercise Guidelines
When designing a stroke recovery exercise program, it is important to prioritize safety and follow proper guidelines. Here are some key points to consider:
By following these safe exercise guidelines, stroke survivors and their caregivers can ensure that exercise is a beneficial and enjoyable part of the recovery journey. Always prioritize safety and work closely with healthcare professionals to design an exercise program tailored to individual needs and goals.
Understanding Left Side Stroke Effects
When an individual experiences a left side stroke, it can result in various effects on the body. Understanding these effects is crucial for caregivers assisting in the recovery process. Two significant areas impacted by a left side stroke include hemiparesis and language impairments.
Hemiparesis and Hemiplegia
Following a left side stroke, an individual may experience hemiparesis, which refers to muscle weakness on the opposite half of the body. In the case of a left side stroke, this weakness affects the right side of the body. Hemiparesis can significantly impact mobility, making it challenging for individuals to perform daily activities, such as walking, bathing, dressing, and toileting. In more severe cases, a left side stroke can lead to hemiplegia, which is the paralysis of the right half of the body [3].
Language Impairments and Speech Difficulties
One of the most common effects of a left side stroke is language impairment. Aphasia, the inability to process or produce language, is frequently observed after a left side stroke [3]. This condition significantly affects communication and can make it challenging for individuals to express themselves or understand spoken or written language. Another language-related impairment that can occur after a left side stroke is apraxia of speech. Apraxia of speech is a sound disorder that hinders an individual's ability to form sounds and words due to impaired control of speech muscles [3].
It's important for caregivers to be aware of these language impairments and provide support and patience during communication. Utilizing alternative forms of communication, such as gestures, pictures, or assistive devices, can help bridge the gap and enhance communication with individuals recovering from a left side stroke.
In addition to hemiparesis and language impairments, other effects of a left side stroke may include dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) and other cognitive and emotional changes. It's crucial for caregivers to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive care plan tailored to the individual's specific needs. By understanding the effects of a left side stroke, caregivers can provide the necessary support and assistance to promote recovery and improve the quality of life for stroke survivors.
Physical Exercises for Stroke Recovery
Engaging in physical exercises is crucial for stroke recovery, especially when it comes to rehabilitating the left side of the body. The following exercises target various areas affected by left side stroke, including the legs, core stability and balance, arm and shoulder, as well as hand and finger strength.
Leg Strengthening Exercises
Leg exercises play a vital role in improving strength, gait, and balance for stroke survivors. By focusing on leg muscles, individuals can regain mobility and reduce the risk of falling. Here are a few leg strengthening exercises that can be practiced at home:
ExerciseDescriptionKnee ExtensionsSit on a chair with both feet flat on the floor. Slowly extend one leg forward, keeping the knee straight, and hold for a few seconds. Return to the starting position and repeat with the other leg.Seated MarchingSit on a chair with both feet flat on the floor. Lift one leg, bending the knee, and bring it back down. Alternate legs in a marching motion.
Core Stability and Balance Exercises
Improving core stability and balance is essential for enhancing gait and reducing the risk of falls. These exercises target the trunk and core muscles, helping stroke survivors regain control and confidence in their movements. Here are a couple of examples:
ExerciseDescriptionTrunk Rotation (Twists)Sit on a chair with your feet flat on the floor. Place your hands on your shoulders. Slowly rotate your upper body to the left, then to the right, keeping your hips and legs stable.Knee to ChestLie on your back with your legs extended. Slowly bring one knee toward your chest, using both hands to assist if needed. Hold for a few seconds, then return to the starting position. Repeat with the other leg.
Exercise descriptions adapted from Flint Rehab.
Arm and Shoulder Rehabilitation Exercises
Recovering arm and shoulder strength is essential for regaining independence in daily activities. These exercises focus on rebuilding muscle strength and coordination. Here are a couple of arm and shoulder exercises that can be practiced at home:
ExerciseDescriptionTabletop CircleSit or stand with your arms bent at a 90-degree angle, as if resting on a table. Slowly move your arms in a circular motion, clockwise and counterclockwise. Focus on maintaining control and stability throughout the movement.Unweighted Bicep CurlsStand or sit with your arms hanging by your sides, palms facing forward. Slowly bend your elbows, bringing your hands towards your shoulders. Return to the starting position and repeat.
Exercise descriptions adapted from Flint Rehab.
Hand and Finger Strengthening Exercises
Hand and finger exercises are particularly beneficial for stroke recovery, as they target fine motor coordination and dexterity. These exercises help regain control and precision in movements. Here are a couple of hand and finger strengthening exercises that can be practiced at home:
ExerciseDescriptionHand Surface StretchPlace your affected hand flat on a table or other flat surface. Slowly move your fingers apart, stretching the webbing between them. Hold for a few seconds, then relax. Repeat several times.Wrist Flexion and ExtensionSit or stand with your arms extended in front of you. Slowly bend your wrist upward, bringing your fingers towards your forearm. Return to the starting position and then bend your wrist downward, extending your fingers away from your forearm. Repeat the flexion and extension movements.
Exercise descriptions adapted from Flint Rehab.
By incorporating these physical exercises into a stroke recovery routine, individuals can make significant progress in regaining strength, mobility, and function on the left side of the body. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to ensure exercises are performed safely and effectively.
Advanced Stroke Recovery Exercises
As stroke survivors progress in their rehabilitation journey, advanced exercises become an important part of their recovery process. These exercises focus on specific areas, such as core strengthening for trunk control, and take advantage of the brain's neuroplasticity to enhance recovery.
Core Strengthening for Trunk Control
Core exercises for stroke patients play a vital role in improving stability throughout the body, which in turn enhances balance and gait [4]. Building strength and coordination in the core muscles helps reduce the risk of falling and prevents further injury or complications.
When a stroke occurs, it can damage the areas of the brain responsible for controlling movement on the opposite side of the body, leading to hemiparesis or hemiplegia [4]. By focusing on core strengthening exercises, stroke survivors can regain control and stability in their trunk, which can positively impact their overall motor function and quality of life.
It is crucial to work closely with a therapist to ensure that these exercises are suitable for your specific needs and abilities. They can provide guidance on how to modify the exercises based on your level of ability, ensuring safety and effectiveness.
Neuroplasticity and Exercise Benefits
Neuroplasticity refers to the brain's ability to rewire itself and heal after an injury such as a stroke. Through neuroplasticity, neural connections are created and strengthened, improving communication between the brain and the affected muscles. This leads to better trunk control, dynamic balance, standing balance, posture, and gait.
Advanced stroke recovery exercises take advantage of neuroplasticity by challenging the brain and body to adapt and improve. These exercises promote the development of new neural pathways and the reestablishment of motor skills. By consistently engaging in advanced exercises under the guidance of a therapist, stroke survivors can optimize their recovery and regain function in their trunk and other affected areas.
Remember, the advanced stroke recovery exercises should only be attempted once you have regained enough strength and coordination in your core. It's essential to consult with your therapist to determine if these exercises are suitable for your specific condition and receive any necessary modifications.
By incorporating core strengthening exercises for trunk control and leveraging the brain's neuroplasticity, stroke survivors can continue to make progress in their recovery and improve their overall function and quality of life.
Safety Tips for Stroke Exercises
When engaging in stroke recovery exercises, it is essential to prioritize safety to prevent any potential harm or injury. By following certain guidelines and incorporating proper stretching and warm-up techniques, caregivers can ensure a safe and effective exercise routine for seniors recovering from a left side stroke.
Avoiding Harmful Exercises
To protect the individual's well-being, it is crucial to avoid exercises that may pose risks or exacerbate existing conditions. Here are some examples of exercises that should be avoided:
Exercises to AvoidReasonBouncing during stretching (ballistic stretching)Bouncing while stretching can cause small tears in the muscle tissue, leading to muscle soreness or tenderness. Instead, opt for static stretching without bouncing.Full squatsFull squats that push the knee joint past 90 degrees can strain ligaments, cartilage, muscles of the knee joint, and lower back, potentially causing problems with the tracking of the kneecap. Consider alternative exercises to prevent injuries.Double leg raisesDouble leg raises place significant stress on the lower back, increasing the risk of injury. It is recommended to perform the exercise one leg at a time, keeping the hips stable throughout the movement and bending the other leg with the foot on the ground as alternatives.Behind the neck press or lat pulldown behind the neckExercises involving behind the neck movements, such as behind the neck press or lat pulldown, should be avoided, especially if the individual has shoulder instability. These exercises may put unnecessary strain on the shoulders, potentially leading to injuries. It is advisable to steer clear of these exercises to prevent any potential harm.
Importance of Stretching and Warm-Up
Stretching, warm-up exercises, and cool-down routines are crucial components of exercise safety. While they may not completely prevent injuries, they provide several benefits, including reducing muscle soreness and preparing individuals mentally for exercise or relaxation post-workout.
Before starting any stroke recovery exercises, it is important to perform gentle stretching exercises to improve flexibility and prepare the muscles for activity. Focus on stretching the muscles that will be targeted during the exercise routine, such as the legs, arms, and shoulders.
A proper warm-up is also essential to increase blood flow to the muscles, raise body temperature, and prepare the cardiovascular system for exercise. This can be accomplished through low-intensity aerobic activities, such as brisk walking or stationary cycling, for approximately 5-10 minutes.
After completing the exercise routine, a cool-down period should be incorporated to gradually reduce heart rate and prevent blood pooling in the extremities. This can be achieved by performing gentle stretches and allowing the body to gradually return to a resting state.
By emphasizing the importance of stretching, warm-up exercises, and cool-down routines, caregivers can ensure the well-being and safety of seniors during their stroke recovery exercises.
Remember, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist for personalized exercise recommendations and guidance based on the individual's specific condition and recovery stage.
Time and Rehabilitation After Stroke
Impact of Rehabilitation Duration
The duration of rehabilitation after a left side stroke plays a crucial role in the recovery process. Studies have shown that the time spent in rehabilitation can have a significant impact on measures of activity and overall outcomes for stroke survivors. It is important to note that the concept of "time" in this context encompasses factors such as rehabilitation intensity, number of repetitions, and physiological effort exerted during the rehabilitation process.
Research has highlighted the global health significance of stroke, with millions of stroke survivors worldwide facing disabilities and a subsequent impact on their quality of life and the lives of their caregivers. Therefore, the duration of rehabilitation becomes a crucial factor in improving functional abilities and reducing dependence.
While the type and content of therapy are important, intervention studies suggest that the time spent in rehabilitation holds greater significance. For instance, studies comparing different types of rehabilitation interventions have shown that as long as the rehabilitation provided is of equal duration, the specific type of therapy may not have a significant impact on overall outcomes. However, it is worth considering that the timing of the intervention may also play a role. It has been observed that providing a greater dose of a specific therapy early after stroke may have a detrimental effect on activities of daily living outcomes.
Multi-Dimensional Stroke Rehabilitation Process
Stroke rehabilitation is a multi-dimensional process that aims to facilitate restitution or substitution of limitations caused by a stroke. It typically follows a four-stage process: assessment of needs, goal setting, intervention, and reassessment [6]. Each stage plays a crucial role in tailoring the rehabilitation program to the individual needs of the stroke survivor.
By following this multi-dimensional rehabilitation process and considering the impact of rehabilitation duration, stroke survivors can maximize their recovery potential and regain independence in their daily lives. It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized rehabilitation plan that suits the individual's needs and goals.
References
[2]:
[3]:
[4]:
[5]:
[6]: