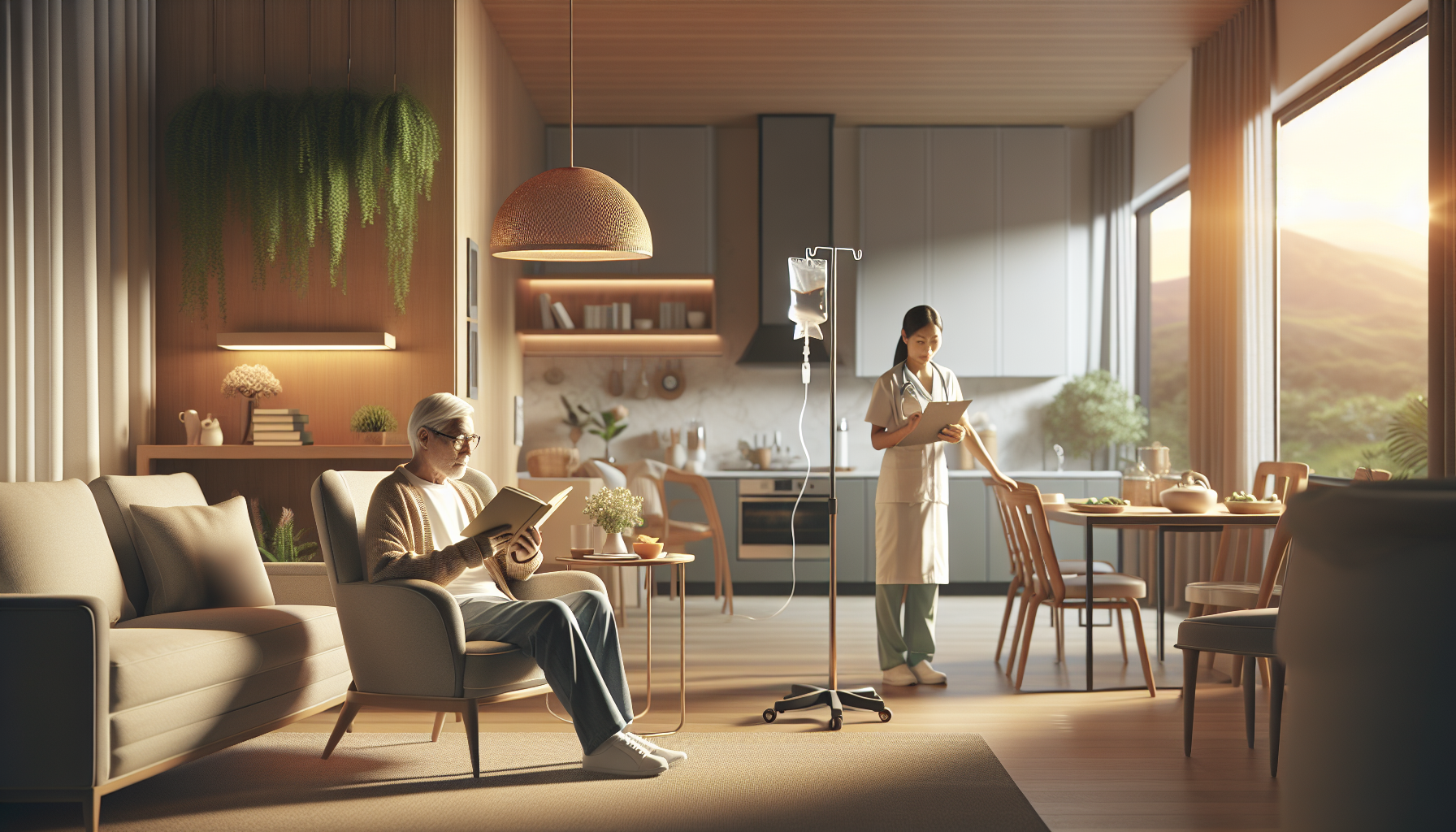
How Can Remote Telemedicine Options Benefit Home Care?
Discover improved access, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced patient experience.

Access to Telemedicine Services
In order to fully benefit from telemedicine services in home care, it is important to address certain barriers and challenges that patients may face. This section focuses on overcoming language barriers, addressing vision and hearing challenges, and enhancing digital literacy to ensure equal access to telemedicine services.
Overcoming Language Barriers
Patients with limited English language skills, known as limited English proficiency (LEP) patients, may find it difficult to understand telemedicine visits conducted in English. It is crucial to provide meaningful access for LEP patients through language services such as oral interpretation and written translation. This is an essential step in ensuring that language does not become a barrier to receiving quality healthcare.

Addressing Vision and Hearing Challenges
Some older patients and individuals with disabilities may face challenges accessing telehealth services due to vision and/or hearing impairments, low skill or comfort level with technology, or cognitive impairment. It is important to provide patient support services and make resources more accessible to address these challenges. For example, offering closed captioning or sign language interpretation for patients with hearing impairment can enhance their ability to engage effectively in telemedicine visits. Similarly, providing larger text sizes or screen reader compatibility for patients with visual impairments can improve their experience with telemedicine.
Enhancing Digital Literacy
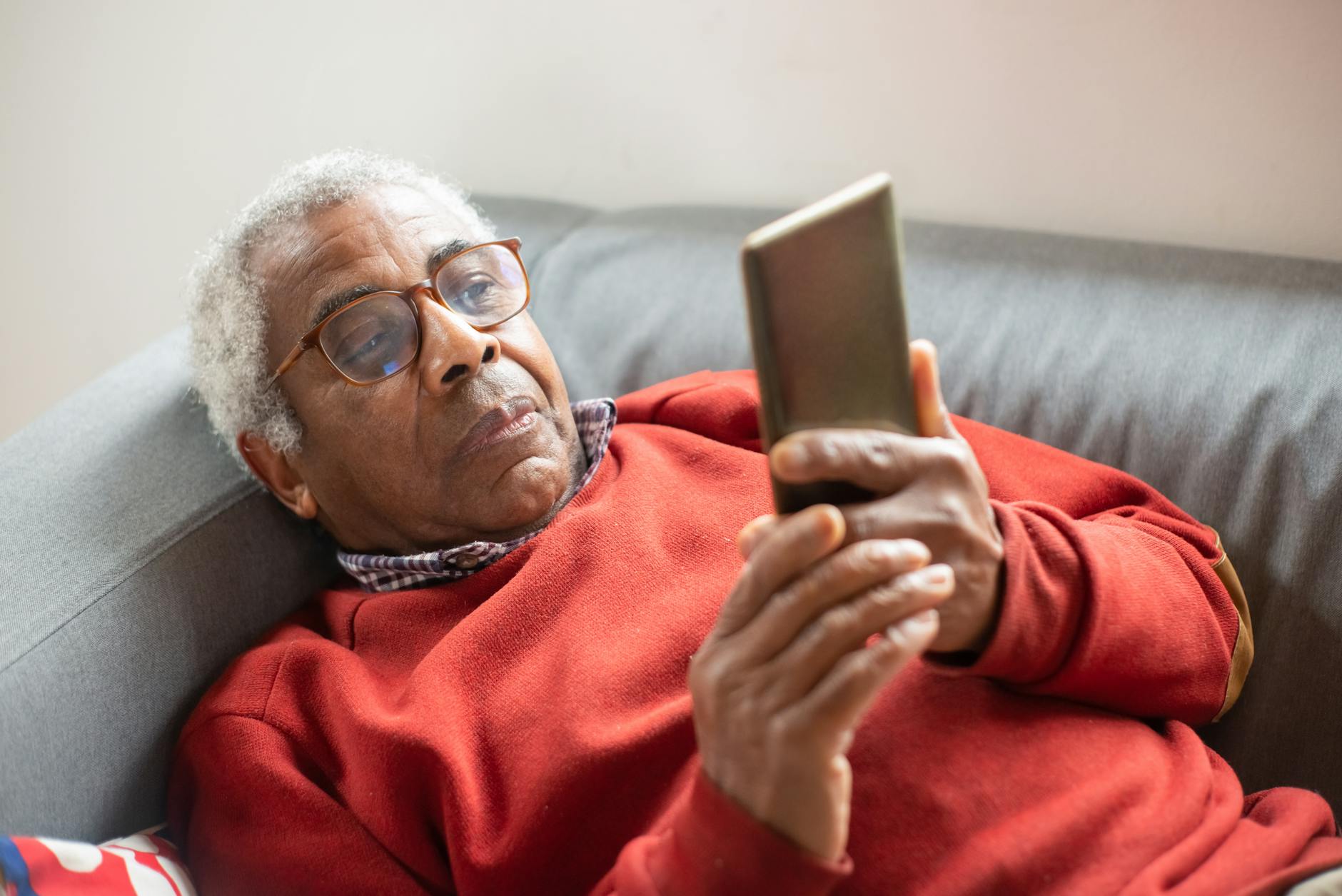
Even with access to a computer, some patients may have questions or feel uncomfortable about managing their health over video when they are used to meeting providers in person. Digital literacy is essential for effective patient-provider communication and collaboration in telemedicine. It is important to provide additional resources and support to patients to improve their digital literacy skills and ensure they can navigate telehealth effectively. This can include providing user-friendly educational materials, offering training sessions, or connecting patients with technology assistance programs to address any concerns or uncertainties they may have.
By actively addressing language barriers, vision and hearing challenges, and enhancing digital literacy, healthcare providers can ensure that all patients, regardless of their individual circumstances, have equal access to telemedicine services in home care. This commitment to inclusivity and accessibility is vital in providing comprehensive and equitable healthcare to all individuals.
Ensuring Equal Access
In order to fully benefit from remote telemedicine options in home care, it is important to ensure equal access for all patients. This includes addressing the needs of individuals with disabilities, adapting to patients' specific requirements, and providing additional support when necessary.
Federal Disability Discrimination Laws
Patients with disabilities are protected by federal laws, such as the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 (Section 504) and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). These laws prohibit discrimination and ensure equal access to healthcare services. Healthcare providers should familiarize themselves with these laws to ensure compliance and to provide reasonable accommodations for patients with disabilities. By modifying procedures and providing additional support, equal access to telehealth services can be ensured before, during, and after virtual visits. (Health Equity in Telehealth)
Adapting to Patients' Needs
Some older patients may face challenges accessing telehealth services due to hearing and/or vision challenges, low skill or comfort level with technology, or cognitive impairment. To address these challenges, healthcare providers can offer more patient support services and make patient resources more accessible. This may include providing assistance with technology setup, offering user-friendly telehealth platforms, and ensuring clear communication during virtual visits. By adapting to the specific needs of patients, barriers to access can be minimized. (Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA))
Providing Additional Support
To ensure equal access to telemedicine, it is crucial to consider patients with limited English language skills or limited English proficiency (LEP). Language services such as oral interpretation and written translation should be provided to ensure meaningful access for LEP patients. This enables patients to fully understand and participate in telemedicine visits, promoting effective communication and equitable care. By removing language barriers, healthcare providers can ensure that LEP patients receive the same level of care as those who are proficient in English. (Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA))
Additionally, access to telemedicine can be limited for individuals with low digital literacy. Patients who are unfamiliar or uncomfortable with technology may require additional resources and support to navigate telehealth effectively. Healthcare providers should offer educational materials, user-friendly telehealth platforms, and assistance with technical issues to help patients overcome these barriers. By providing the necessary support, patients with low digital literacy can gain confidence in utilizing telemedicine services. (Health Equity in Telehealth)
By ensuring equal access for all patients, regardless of their abilities, language skills, or comfort with technology, the benefits of remote telemedicine options in home care can be extended to a wider range of individuals. It is essential for healthcare providers to proactively address these access barriers and provide the necessary accommodations and support to enable equitable care for all patients.
Benefits of Telemedicine in Home Care
Telemedicine offers numerous benefits in the context of home care, providing enhanced care and convenience for both patients and caregivers. In this section, we will explore three key benefits of telemedicine in home care: remote patient monitoring, improved care management, and cost-effectiveness.
Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote patient monitoring plays a crucial role in home care, allowing healthcare providers to effectively manage acute and chronic conditions without requiring patients to travel to medical facilities. By leveraging various devices, patients can monitor their health from the comfort of their own homes, reducing travel costs and minimizing the risk of infection.
This form of monitoring is particularly beneficial for patients who are unable to easily travel or require continuous monitoring for specific health conditions. Remote patient monitoring helps prevent health complications by enabling healthcare providers to track and manage symptoms and conditions remotely. It encompasses a range of devices, from familiar ones like blood pressure monitors to more complex ones that may require patient training.
Remote Patient Monitoring BenefitsAllows for the monitoring of acute and chronic conditions from homeReduces travel costs and minimizes infection riskHelps prevent health complications for patients who can't easily travelEnables tracking of various symptoms and conditions
Improved Care Management
Telemedicine enhances care management in home care settings by providing healthcare providers with real-time access to patient data, facilitating timely interventions and adjustments to treatment plans. This improved access to patient information helps ensure that patients receive the appropriate care at the right time.
With telemedicine, healthcare providers can remotely monitor patients' health metrics, such as blood pressure, heart rate, and glucose levels. This enables early detection of any deviations from normal values, allowing for timely interventions and the prevention of potential health complications. By implementing best practices through remote care management, healthcare providers can optimize patient outcomes and provide personalized care.
Cost-Effectiveness
Telemedicine in home care settings offers cost-effective solutions for both patients and the healthcare system as a whole. By reducing the need for frequent in-person visits or tests, telemedicine helps minimize healthcare expenses associated with travel and facility fees. Patients can save on transportation costs, especially for individuals with limited mobility or those residing in remote areas.
Additionally, telemedicine can help prevent unnecessary hospital admissions and emergency room visits by enabling early intervention and ongoing monitoring of patients' health conditions. By managing chronic conditions remotely, healthcare providers can prevent complications and reduce the overall healthcare costs associated with managing these conditions.
The benefits of telemedicine in home care extend beyond convenience and accessibility. By leveraging remote patient monitoring, improving care management, and offering cost-effective solutions, telemedicine enhances the overall quality of home care, providing patients with improved outcomes and a more comfortable healthcare experience.
Enhancing Patient Experience
Telemedicine offers several advantages that enhance the overall patient experience, providing convenience, increased access to specialists, and quality care.
Convenience of Telehealth
Telehealth appointments eliminate the need for patients to travel to a physical healthcare facility, saving them time and reducing the inconvenience of commuting and waiting in a traditional office setting. This convenience is particularly beneficial for individuals who may have difficulty accessing routine care due to transportation issues or living in remote areas far from healthcare facilities [3]. By utilizing smartphones, tablets, computers, or other connectable devices, patients can connect with healthcare professionals from the comfort of their own homes or workplaces, eliminating the need to take time off work or find childcare.
Increased Access to Specialists
Telemedicine provides patients with greater access to specialists, regardless of their geographic location. Through video calls and remote consultations, individuals can connect with healthcare professionals across various specialties, such as radiologists, oncologists, and neurologists. This increased accessibility is especially valuable for patients in rural or underserved communities who may have limited access to specialized care. Telemedicine enables individuals to receive expert advice and guidance without the need for lengthy travel or relocation.
Quality of Care
Telemedicine appointments offer quality care comparable to in-person visits. Medical professionals can effectively diagnose, treat, and monitor a wide range of healthcare conditions through virtual consultations. Telehealth services have been absorbed into many healthcare networks, with millions of patients in the United States benefiting from telemedicine every year. Moreover, during the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine played a vital role in providing safe and timely care, ensuring that patients could receive necessary medical attention without unnecessary exposure to the virus.
The convenience, increased access to specialists, and quality of care provided by telemedicine make it a valuable tool in enhancing the overall patient experience. By leveraging the benefits of telehealth, caregivers and senior patients can receive comprehensive care from the comfort and convenience of their own homes, improving access to healthcare services and ultimately promoting better health outcomes.
Telemedicine Regulations
Telemedicine has the potential to revolutionize home care by providing remote access to healthcare services. However, there are several regulatory considerations that need to be addressed to ensure the successful implementation of telemedicine in home care settings. This section explores three key aspects of telemedicine regulations: barriers to telemedicine, licensing and practice regulations, and access to broadband technology.
Barriers to Telemedicine
Despite its numerous benefits, telemedicine faces several barriers that hinder its widespread adoption. These barriers include financial constraints, regulatory hurdles, exaggerated expectations, slow adoption rates, technological limitations, lack of evidence-based research, and concerns about the success of telemedicine initiatives. Reimbursement is a common obstacle, as Medicare reimbursement for telemedicine services is often limited to nonmetropolitan areas, specific institutions, and certain CPT codes. Overcoming these barriers requires collaboration between healthcare providers, policymakers, and insurance companies to establish supportive reimbursement policies and regulations.
Licensing and Practice Regulations
Licensing and practice regulations play a crucial role in determining the feasibility of telemedicine services. As telemedicine expands across state lines, licensing becomes a significant barrier. Many state medical boards still require an in-person consultation before initiating telemedicine services, hindering the potential for remote healthcare delivery. Addressing licensing challenges requires policy changes that facilitate interstate practice while maintaining patient safety and quality of care. Streamlining licensing processes and establishing reciprocity agreements between states can help overcome these barriers.
Access to Broadband Technology
Access to reliable broadband technology is fundamental for the success of telemedicine, particularly in rural and underserved areas. Unfortunately, the lack of broadband infrastructure remains a significant barrier to telehealth and health information exchange [4]. While the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has programs in place to support rural healthcare and broadband infrastructure, there are still significant gaps in access to broadband services. Bridging this digital divide requires continued investment in broadband infrastructure, especially in rural and underserved communities, to ensure equitable access to telemedicine services.
It is essential for policymakers to address these regulatory considerations to facilitate the widespread adoption of telemedicine in home care settings. By addressing barriers, streamlining licensing processes, and improving access to broadband technology, telemedicine can fulfill its potential to enhance healthcare delivery, improve patient outcomes, and increase accessibility to quality care.
Future of Telemedicine
As telemedicine continues to evolve, several areas are being explored to enhance remote healthcare services. In this section, we will discuss three aspects that hold promise for the future of telemedicine: remote communication services, evaluating healthcare quality, and enhancing remote communication modes.
Remote Communication Services
Remote communication services play a vital role in facilitating patient-GP interactions in telemedicine. According to a study conducted in Israel, patients perceive online modes of communication, such as structured routes via healthcare service organization (HSO) websites, as providing near-optimal healthcare quality. This mode of communication meets several criteria related to healthcare quality and elicits a high degree of confidence among patients.
To ensure optimal healthcare service quality, policymakers should focus on improving remote communication services. By enhancing the usability, functionality, and accessibility of HSO websites, patients can benefit from a more coherent conveyance of medical issues and clear guidance from GPs. Additionally, integrating services, creating patient portfolios, and increasing patient awareness of available medical management options can further enhance the remote communication experience.
Evaluating Healthcare Quality
Evaluating healthcare quality in remote settings is crucial for providing effective telemedicine services. Studies have shown that patients prioritize convenience over service quality when choosing the mode of remote communication. However, policymakers and healthcare organizations should strive to strike a balance between convenience and quality to deliver optimal care.
Implementing standardized quality evaluation measures can help assess the effectiveness of remote healthcare. By monitoring patient satisfaction, clinical outcomes, and adherence to best practices, healthcare providers can identify areas for improvement and ensure that telemedicine services meet the highest standards of care.
Enhancing Remote Communication Modes
To further improve the future of telemedicine, there is a need to enhance remote communication modes. Asynchronous online modes of patient-GP communication have gained popularity, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, these modes can sometimes hinder the physician's understanding of the patient's clinical issues and the patient's comprehension of the recommended treatment plan [5].
To address these challenges, policymakers and healthcare organizations should invest in technologies that enable real-time, synchronous communication. By incorporating video consultations and interactive platforms, healthcare providers can better understand patients' needs, effectively convey medical information, and foster a stronger patient-provider relationship. This can lead to improved healthcare outcomes and a more satisfying telemedicine experience for both patients and GPs.
As telemedicine continues to advance, the future holds great potential for remote communication services, evaluating healthcare quality, and enhancing remote communication modes. By focusing on these areas, telemedicine can provide even greater convenience, access to care, and improved healthcare outcomes for patients receiving home care.
References
[2]:
[3]:
[4]:
[5]: