50+ Failure To Thrive Elderly Life Expectancy Statistics
Learn about FTT and how early intervention and social support can lead to better outcomes.
.jpg)
Failure To Thrive Elderly Life Expectancy Statistics
As the population ages, failure to thrive (FTT) among the elderly is becoming a growing concern. FTT is defined as a decline in physical, psychological, and/or cognitive function that is not due to a specific disease or condition. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including social isolation, malnutrition, medication side effects, and depression.

General Statistics
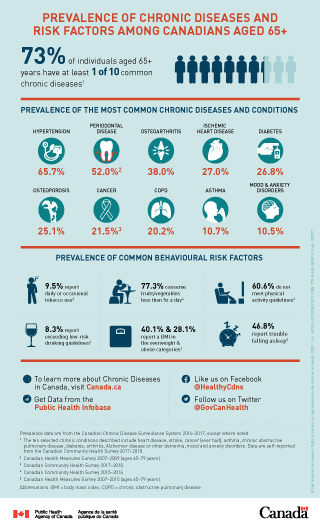
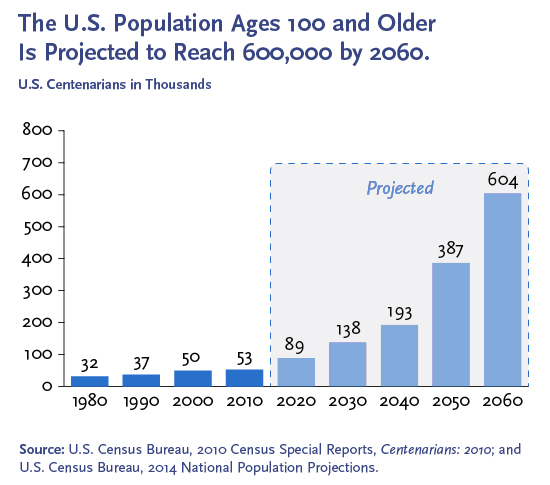
- FTT affects between 5% and 50% of elderly individuals.
- The prevalence of FTT increases with age, with rates as high as 50% in those over the age of 85.
- FTT is more common in women than in men.
- FTT is associated with increased healthcare costs and hospitalization rates.
Life Expectancy
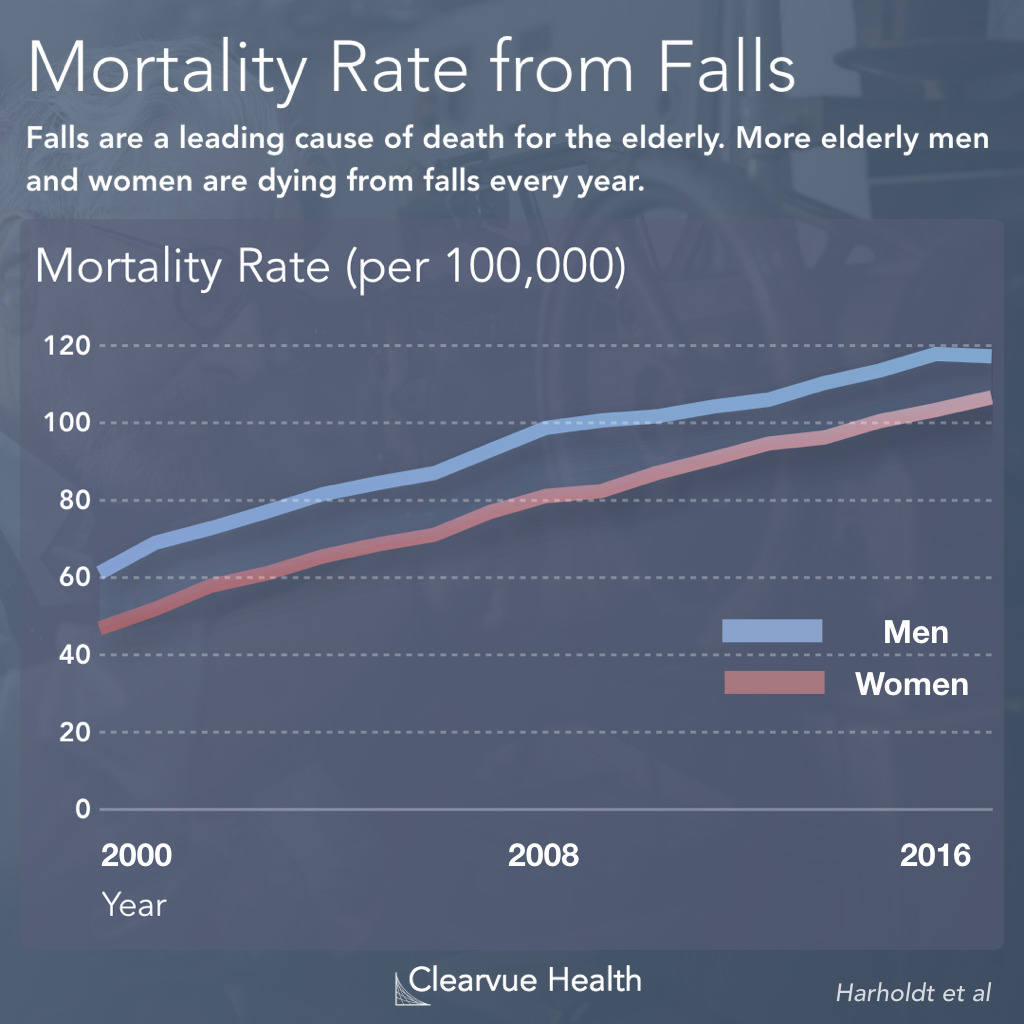
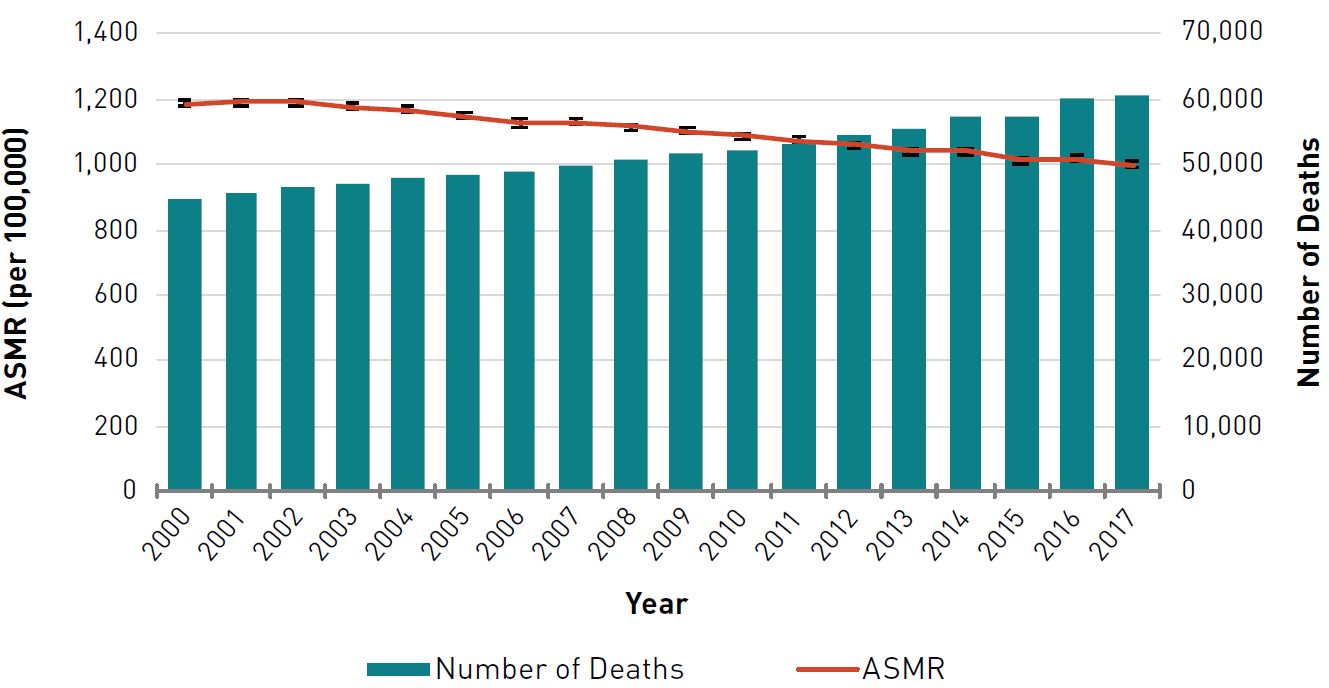
- Elderly individuals with FTT have a higher risk of mortality than those without FTT.
- The life expectancy of elderly individuals with FTT is significantly shorter than those without FTT.
- The survival rate of elderly individuals with FTT is lower than those without FTT.
- The mortality rate of elderly individuals with FTT is higher than those without FTT.
Risk Factors
- Social isolation is a significant risk factor for FTT.
- Malnutrition is a significant risk factor for FTT.
- Depression is a significant risk factor for FTT.
- Medication side effects are a significant risk factor for FTT.
Treatment
- Early identification and intervention can improve outcomes for elderly individuals with FTT.
- Nutritional interventions, such as dietary supplements and meal assistance, can improve outcomes for elderly individuals with FTT.
- Social interventions, such as social support and engagement, can improve outcomes for elderly individuals with FTT.
- Medication management can improve outcomes for elderly individuals with FTT.
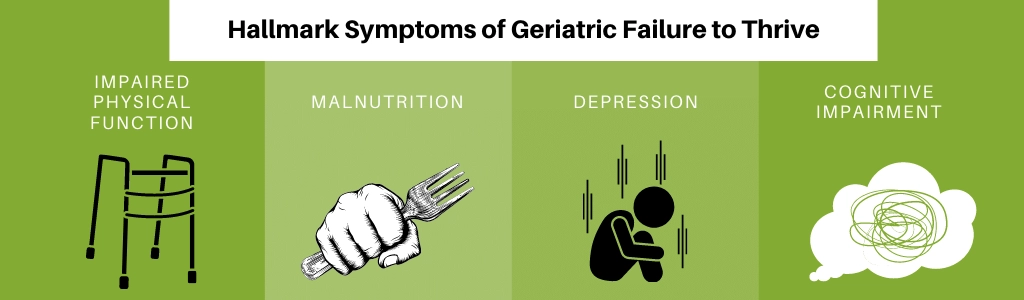
Causes
Physical and mental decline is a common concern. But other factors can also impact our ability to thrive. Lack of social interaction and medical care can lead to isolation and poor health. Making healthy choices, like exercising and eating well, can increase our chances of living a long and happy life.
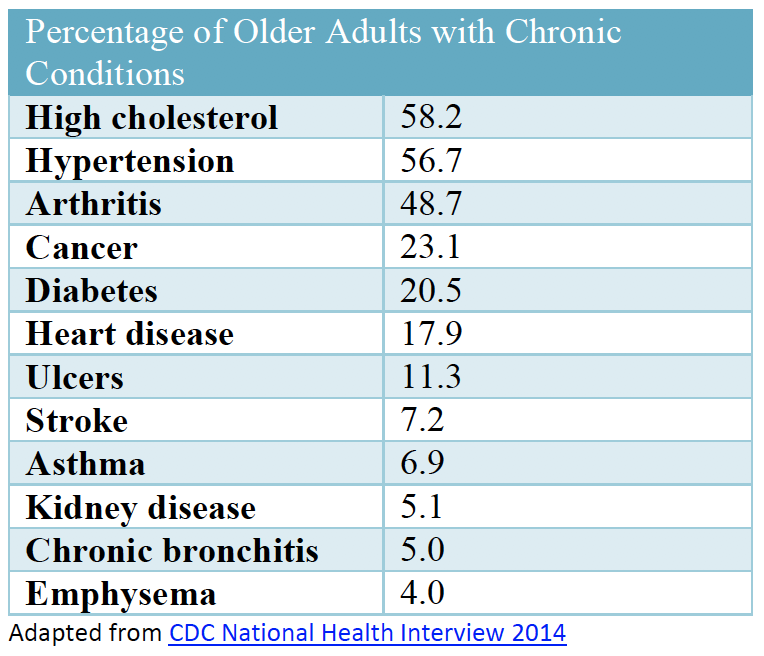
- FTT can be caused by a variety of factors, including chronic illness, disability, cognitive impairment, and poor oral health.
- In some cases, FTT may be related to financial constraints or inadequate access to food and resources.
Prevention
- Regular medical check-ups can help identify early signs of FTT and prevent further decline.
- Encouraging social connections and participation in activities can help reduce the risk of social isolation and depression.
- Providing access to nutritious food and assistance with meal preparation can help prevent malnutrition and improve overall health.
Diagnosis
As we age, we may face health issues that can affect our quality of life, including failure to thrive. This condition can lead to a decline in physical, psychological, or social function, resulting in a lower quality of life and decreased life expectancy. Factors that contribute to this condition include chronic illness, malnutrition, social isolation, and depression. To address it effectively, it's important to recognize the signs early on and make appropriate lifestyle changes.
- Diagnosis of FTT typically involves a comprehensive medical assessment to identify potential underlying causes.
- This may include laboratory tests, nutritional assessments, and evaluations for cognitive impairment and mental health issues.
Management
- Treatment for FTT often involves a multidisciplinary approach that addresses both medical and social factors.
- In addition to nutritional interventions, medication management, and social support, physical therapy and rehabilitation may be recommended to improve strength and mobility.
- In some cases, surgery or other medical interventions may be necessary to address underlying health issues contributing to FTT.
Prognosis
- The prognosis for individuals with FTT varies depending on the severity of the condition and underlying factors.
- Early identification and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for those with FTT, while delayed treatment may result in further decline and reduced life expectancy.
Complications
- FTT can lead to a variety of complications, including increased risk of infections, pressure ulcers, and falls.
- Individuals with FTT may also experience cognitive decline, weakness, and functional impairment.
Caregiving
- Caregivers play an important role in the management and treatment of FTT.
- Providing emotional support, assistance with daily activities, and monitoring for signs of decline can help improve outcomes for individuals with FTT.
Research
- Ongoing research is focused on identifying new strategies for preventing and treating FTT.
- This includes investigating the use of technology-based interventions, such as telemedicine and mobile health apps, to improve access to care and support for individuals with FTT.
Public Health Implications
- The high prevalence of FTT among elderly individuals highlights the need for greater awareness and education about this condition.
- Addressing risk factors and providing effective interventions for FTT could have significant public health benefits, including reducing healthcare costs and improving quality of life for older adults.
Ethical Considerations
- The management of FTT raises important ethical considerations related to decision-making and autonomy.
- In some cases, individuals with FTT may refuse medical treatment or interventions, raising questions about the right to self-determination and the duty of care.
End-of-Life Care
- FTT is often considered a hallmark of end-of-life care, as it can be a sign of natural decline and approaching death.
- Providing compassionate care and support for individuals with FTT at the end of life is an important aspect of palliative care.
Global Health Implications
- FTT is a global health issue that affects elderly individuals in both developed and developing countries.
- Addressing FTT requires a multifaceted approach that considers social, economic, and cultural factors in addition to medical interventions.
Education and Training
- Providing education and training for healthcare providers, caregivers, and family members can help improve awareness and understanding of FTT.
- This can include training on identifying risk factors, implementing interventions, and providing compassionate care for individuals with FTT.
Policy Implications
- The high prevalence and significant health impacts of FTT highlight the need for policy-level interventions to address this issue.
- This may include initiatives to increase access to nutritious food and resources, support for caregivers, and incentives for healthcare providers to identify and manage cases of FTT.
Collaboration and Coordination
- Addressing FTT requires collaboration and coordination across healthcare settings and disciplines.
- This includes communication and information-sharing between primary care providers, specialists, and other healthcare professionals involved in the care of individuals with FTT.
Health Equity
- FTT is a health equity issue, as it disproportionately affects vulnerable populations, including those with low income, limited access to healthcare, and social isolation.
- Addressing FTT requires a focus on health equity and addressing systemic barriers to care and resources.
Technology
- Technology-based interventions, such as telemedicine and remote monitoring, may offer new opportunities for identifying and managing cases of FTT.
- These interventions may be particularly useful for individuals who have limited access to healthcare or who live in rural or remote areas.
Innovation
- Ongoing innovation is needed to identify new approaches for preventing and treating FTT.
- This may include the development of new nutritional supplements, medical devices, or technologies that can improve the delivery of care and support for individuals with FTT.
Advocacy
- Advocacy efforts can help raise awareness about FTT and promote policies and programs that support the prevention and management of this condition.
- This includes advocating for increased funding for research, education, and community-based interventions that address the needs of elderly individuals with FTT.
Promoting Longevity in the Elderly
To enhance the life expectancy and overall well-being of the elderly, it is important to focus on certain key aspects. Promoting healthy lifestyle choices, emphasizing the importance of social connections, and ensuring access to quality healthcare are all crucial factors in supporting longevity in the elderly population.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Encouraging and enabling the elderly to make healthy lifestyle choices can significantly impact their longevity. This includes engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet, getting sufficient sleep, and avoiding harmful habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Regular exercise, tailored to individual capabilities, can improve cardiovascular health, strengthen muscles and bones, and enhance overall mobility and well-being. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats provides essential nutrients and helps prevent chronic diseases commonly associated with aging.
Ensure that the elderly have access to resources that educate them on healthy eating habits, exercise routines, and other beneficial lifestyle choices. This can be achieved through community programs, healthcare professionals, and online resources.
Importance of Social Connections
Maintaining social connections is vital for the mental and emotional well-being of the elderly. Loneliness and social isolation can negatively impact health outcomes and decrease life expectancy. Encouraging and facilitating social interactions can help alleviate feelings of loneliness and improve overall quality of life.
Promote involvement in community activities, clubs, and organizations that cater to the interests and needs of the elderly. This fosters a sense of belonging and provides opportunities for social engagement. Family members, friends, and neighbors should also play an active role in supporting and staying connected with the elderly.
Access to Quality Healthcare
Access to quality healthcare is essential for the elderly to effectively manage their health conditions and address any emerging concerns. Regular check-ups, preventive screenings, and timely medical interventions can significantly impact life expectancy.
It is crucial to ensure that the elderly have access to healthcare professionals who specialize in geriatric care and understand the unique needs of older adults. This includes physicians, nurses, physical therapists, and other healthcare providers.
FAQs
What is failure to thrive in the elderly?
Failure to thrive (FTT) is a condition that can occur in older adults, which is characterized by a decline in physical, psychological, or social function. This can result in a lower quality of life and decreased life expectancy.
What are the complications associated with failure to thrive in the elderly?
FTT can lead to a variety of complications such as increased risk of infections, pressure ulcers and falls. Individuals with FTT may also experience cognitive decline, weakness and functional impairment.
How can caregivers help manage failure to thrive in the elderly?
Caregivers play an important role in managing FTT by providing emotional support, assistance with daily activities and monitoring for signs of decline. They can also ensure access to nutritious food and resources.
What is the prognosis for individuals with failure to thrive?
The prognosis for individuals with FTT varies depending on the severity of the condition and underlying factors. Early identification and intervention can significantly improve outcomes while delayed treatment may result in further decline and reduced life expectancy.
Summary
FTT is a significant concern among the elderly population, with high rates of prevalence and increased healthcare costs. Elderly individuals with FTT have a shorter life expectancy and higher mortality rates than those without FTT. Social isolation, malnutrition, depression, and medication side effects are significant risk factors for FTT. Early identification and intervention, along with nutritional and social interventions, can improve outcomes for elderly individuals with FTT.
Sources:
- https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/
- https://griswoldsa.com/failure_to_thrive_in_the_elderly/
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/
- https://www.journalmc.org/index.php/JMC/article/view/