60 Dementia Statistics And Facts
Discover how we can make lives better for those affected by dementia. Join us in raising awareness and funding research efforts.
.jpg)
Dementia Statistics
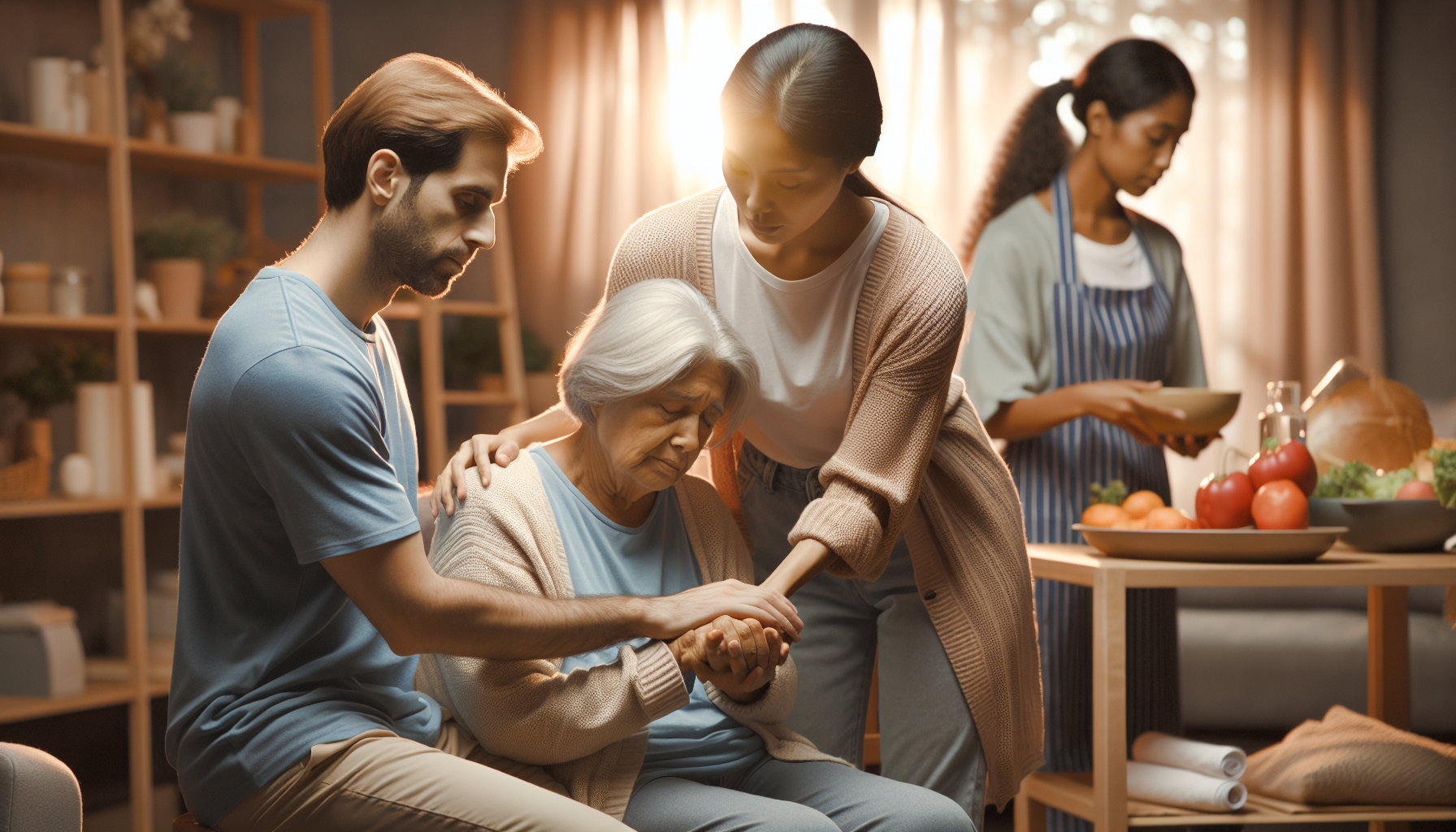
Dementia affects millions worldwide and sadly there is no cure. However, organizations like the Alzheimer's Association provide resources and support.
Early diagnosis of dementia is important for treatment and planning. Signs include forgetfulness, confusion, difficulty communicating, and changes in mood or behavior. Speak with a healthcare professional if you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms. They can provide guidance and support.

Prevalence of Dementia
Dementia is a serious health concern that impacts millions of people around the world, and it has far-reaching implications for our healthcare systems and society as a whole. Unfortunately, women are more likely to be affected by dementia than men, accounting for two-thirds of all cases worldwide. It's important that we work together to raise awareness about this issue and find ways to support those who are affected by dementia, regardless of their gender or background.
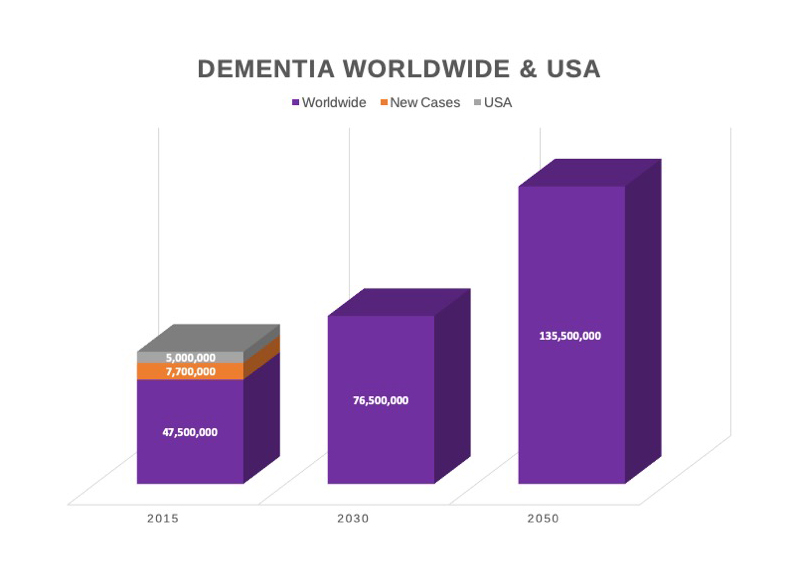
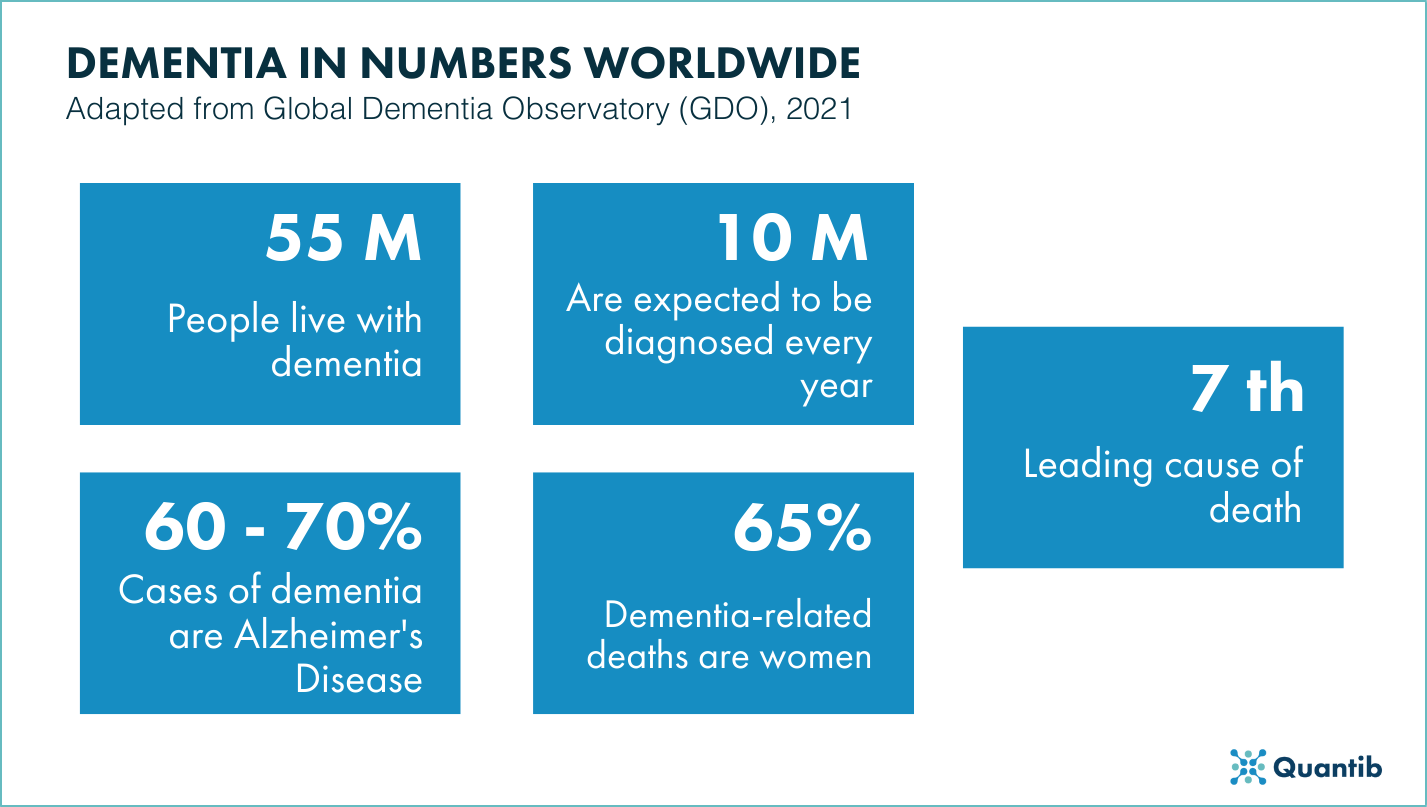
- It is estimated that approximately 55 million people worldwide have dementia. (World Health Organization, 2023)
- In the United States, there are an estimated 6.2 million people with dementia. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
- Dementia is more prevalent in women than in men, with women accounting for approximately two-thirds of dementia cases worldwide. (World Health Organization, 2021)
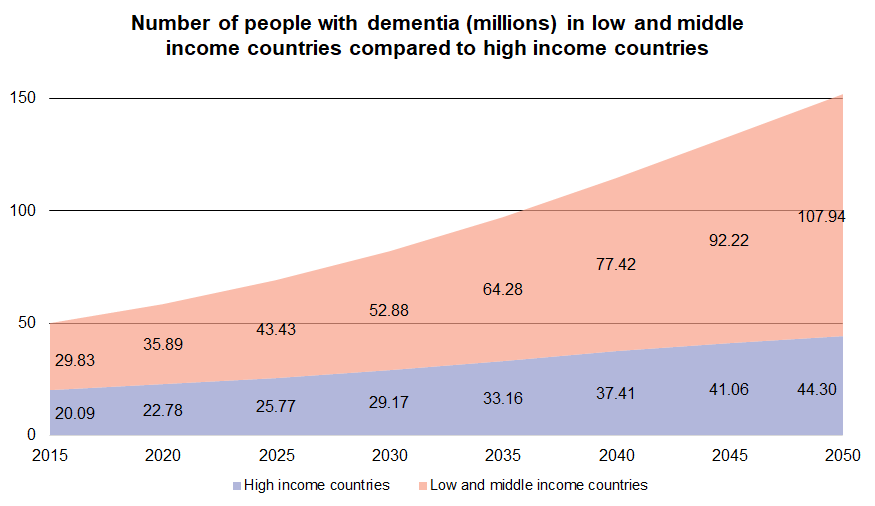
- The number of people with dementia is expected to triple by 2050. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- In the United States, the number of people with dementia is projected to reach 13.8 million by 2050. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)

Impact of Dementia
Despite the growing awareness of dementia, many people are still not fully aware of its effects on our health and well-being, as well as the financial burden it places on families and communities. By shedding light on these issues, we hope to raise awareness and encourage more support for those affected by dementia.
- Dementia is the seventh leading cause of death worldwide. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- In the United States, Alzheimer's disease (the most common form of dementia) is the sixth leading cause of death. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
- Dementia is the leading cause of disability among older adults worldwide. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- Dementia is one of the most costly diseases to society, with estimated global costs of $1 trillion in 2018. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- In the United States, the total cost of caring for people with dementia is estimated to be $355 billion in 2021. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
Living with Dementia
- While there is no cure for dementia, there are treatments and interventions that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Caregiver support and education programs are important for helping those who care for individuals with dementia manage stress and provide effective care.
- Creating a safe and supportive environment for individuals with dementia is important for promoting their independence and improving their quality of life.
Risk and Protective Factors for Dementia
As we age, our risk for dementia increases significantly, but there are also other factors that can contribute to the development of this disease.
- Age is the biggest risk factor for dementia, with the risk increasing significantly after the age of 65. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- Family history of dementia is also a risk factor, with people who have a parent or sibling with dementia being more likely to develop the disease themselves. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
- Education and cognitive activity are protective factors that may reduce the risk of dementia. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- Physical activity and a healthy diet may also reduce the risk of dementia. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- There is some evidence to suggest that social engagement and having a strong social support network may reduce the risk of dementia. (World Health Organization, 2021)
Diagnosis and Treatment of Dementia
For those who have been diagnosed with dementia, it can be a difficult and uncertain time. While there is currently no cure for this disease, there are treatments available that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Early diagnosis is important for providing effective support and planning for the future.
- Early diagnosis of dementia is important for managing symptoms, providing support, and planning for the future. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- There is currently no cure for dementia, but some medications and therapies may help manage symptoms. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
- Medications approved for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease include cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
- Non-drug therapies that may benefit people with dementia include cognitive stimulation therapy, reminiscence therapy, and music therapy. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- Caregiver support and education are essential for people with dementia and their families. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
Dementia and Caregiving
The burden of caregiving can affect the health of caregivers and have a ripple effect on healthcare costs and productivity in the workplace. However, there are resources available such as respite care, support groups, and educational programs that can provide much-needed assistance to caregivers.
- The majority of people with dementia require some form of long-term care. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- Family members provide the majority of care for people with dementia, often at great personal and financial cost. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
- Caregiving for people with dementia can have a significant impact on the physical and mental health of caregivers. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- Respite care, support groups, and education programs can help alleviate the burden of caregiving. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
- Caregiving for people with dementia is associated with higher healthcare costs and lost productivity in the workplace. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
Types of Dementia
- Alzheimer's disease is the most common type of dementia, accounting for 60-80% of cases.
- Other types of dementia include vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, frontotemporal dementia, and mixed dementia.
- Each type of dementia has its own unique symptoms and causes.
Dementia and Diversity
It is important to recognize the unique challenges faced by these diverse populations and to provide culturally sensitive care and support services. In this context, more research is needed to better understand how dementia impacts diverse communities and how we can best address these challenges.
- Dementia disproportionately affects people in low- and middle-income countries, where access to healthcare and support services may be limited. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- People from certain racial and ethnic groups (such as African Americans and Hispanics) may be at higher risk of developing dementia. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
- People from culturally diverse backgrounds may experience stigma and discrimination related to dementia. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- Culturally sensitive care and support services are essential for people with dementia from diverse backgrounds. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- More research is needed to better understand and address the impact of dementia on diverse populations. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
Global Efforts to Address Dementia
There are global efforts underway to address the issue and improve the lives of those impacted by it. From international organizations to public education campaigns, initiatives are being implemented to raise awareness, coordinate research efforts, and develop new treatments for this disease.
- The World Health Organization has identified dementia as a public health priority and has developed a global action plan to address the disease. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- The United States government has launched the National Plan to Address Alzheimer's Disease, which aims to prevent and effectively treat Alzheimer's disease and related dementias by 2025. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
- The World Dementia Council and the Global Alzheimer's and Dementia Action Alliance are international organizations that work to raise awareness and coordinate efforts to address dementia. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- Research is ongoing to better understand the causes of dementia and develop new treatments. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
- Public education and awareness campaigns are important for reducing stigma and promoting early diagnosis and treatment. (World Health Organization, 2021)
Dementia and COVID-19
- The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on individuals with dementia and their caregivers.
- Social isolation and disruptions to routine care can exacerbate symptoms and increase stress for those living with dementia.
- Vaccination against COVID-19 is important for protecting individuals with dementia and reducing the risk of severe illness or death from the disease.
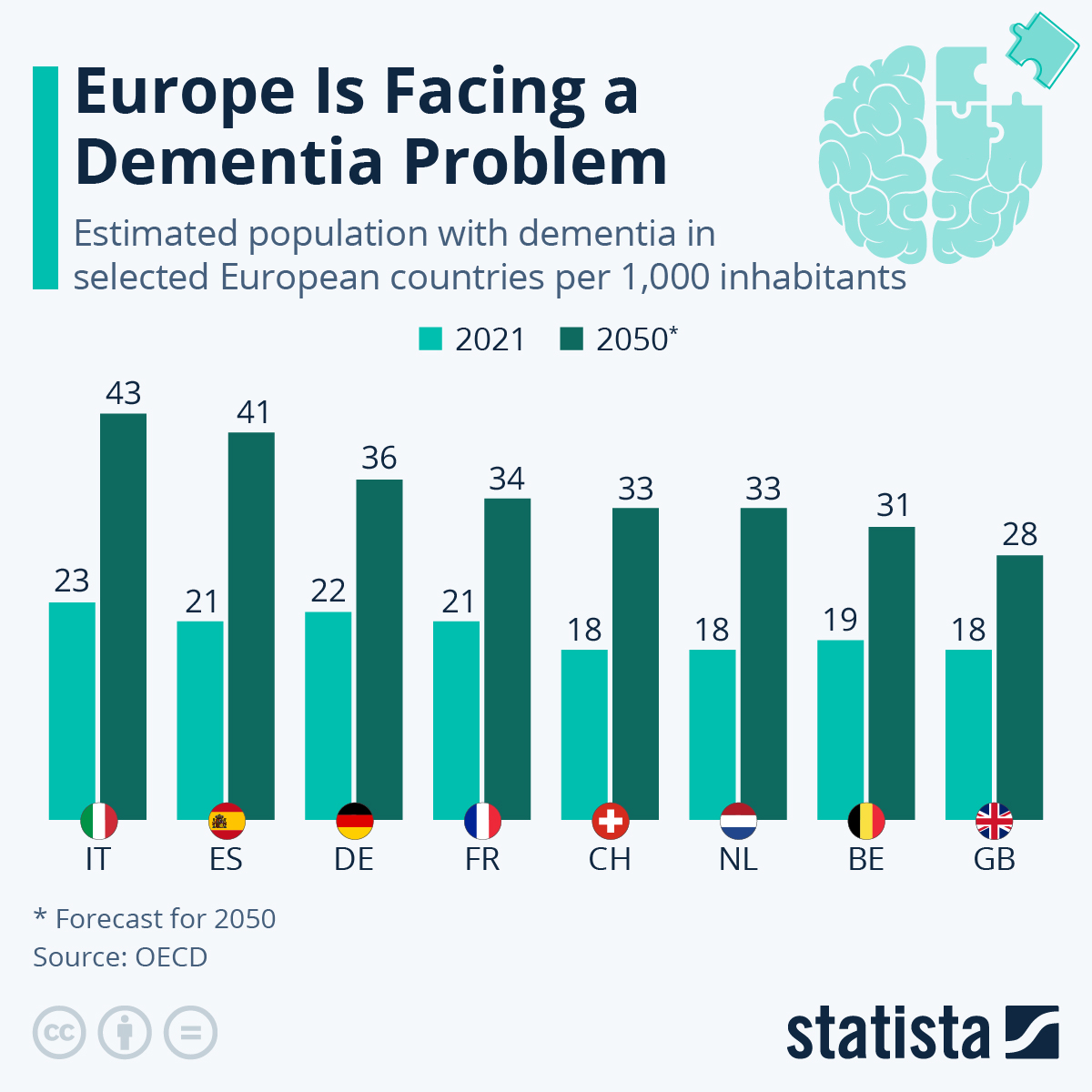
Future Implications of Dementia
The impact of dementia extends beyond individual patients and their families, as it also has significant economic and societal implications. While advancements in technology show promise for new diagnostic and treatment methods, more research is needed to effectively prevent this disease.
- As the global population ages, the number of people with dementia is expected to continue to rise. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- The economic impact of dementia is expected to increase significantly in the coming years. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
- Advances in technology (such as virtual reality and artificial intelligence) may offer new ways to diagnose and treat dementia. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- More research is needed to develop effective prevention strategies for dementia. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
- Dementia is a significant public health challenge that requires ongoing attention and investment at the local, national, and global levels. (World Health Organization, 2021)
Current Treatments and Interventions for Dementia
- There is currently no cure for dementia, but there are medications that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for individuals living with the disease. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
- Non-pharmacological interventions such as cognitive stimulation therapy, physical exercise, and music therapy have been shown to have positive effects on cognitive function and quality of life in individuals with dementia. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- Caregiver support and education programs are important for helping those who care for individuals with dementia manage stress and provide effective care. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
Social and Ethical Considerations in Dementia Care
The stigma surrounding the disease, as well as ethical issues such as informed consent and end-of-life decision making, can have a significant impact on the quality of life for both patients and caregivers.
- The social stigma associated with dementia can lead to discrimination, isolation, and poor quality of life for individuals with the disease. Efforts to raise awareness and reduce stigma are important for promoting social inclusion and improving outcomes in people with dementia. (World Health Organization, 2021)
- Ethical considerations are important when it comes to dementia care, particularly around issues such as informed consent, autonomy, and end-of-life decision making. (Alzheimer's Association, 2021)
- Creating dementia-friendly communities that support the needs of individuals with the disease can improve quality of life for both patients and caregivers. (World Health Organization, 2021)
Risk Factors for Dementia
Understanding the risk factors for dementia is essential for identifying individuals who may be at higher risk of developing the disease and taking steps to prevent or manage it. While age is the primary risk factor for dementia, other factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and medical conditions can also increase an individual's risk. In this text, we will explore some of the key risk factors associated with dementia.
- Age is the biggest risk factor for dementia, with the risk of developing the disease increasing as people get older.
- Genetics can also play a role in the development of dementia, with certain genes increasing the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease.
- Lifestyle factors such as smoking, physical inactivity, and poor diet have been linked to an increased risk of dementia.
- Other medical conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and depression can also increase the risk of developing dementia.
Diagnosing Dementia
- There is no single test that can diagnose dementia. Instead, doctors use a variety of tests and assessments to evaluate a person's cognitive function and rule out other possible causes of their symptoms.
- These tests may include physical exams, cognitive assessments, blood tests, brain imaging scans, and other diagnostic tools.
Research on Dementia
- Research on the causes of dementia is ongoing, with scientists exploring new treatments and prevention strategies.
- Advances in technology (such as virtual reality and artificial intelligence) may offer new ways to diagnose and treat dementia.
- Clinical trials are an important part of dementia research, helping to test new treatments and interventions for the disease.
FAQs
What is dementia?
Dementia is a broad term used to describe a decline in cognitive function that interferes with daily activities. It is not a specific disease, but rather a group of symptoms caused by various underlying conditions.
What are the early signs of dementia?
The early signs of dementia can vary depending on the type and cause of the disease. However, common symptoms include memory loss, difficulty with language and communication, changes in mood or behavior, and decreased ability to plan or organize.
Is there a cure for dementia?
There is currently no cure for dementia, but there are treatments and interventions that can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for individuals living with the disease.
What causes dementia?
Dementia can be caused by a variety of underlying conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia, Lewy body dementia, frontotemporal dementia, and mixed dementia. Other factors such as genetics, lifestyle choices (e.g., smoking), and medical conditions (e.g., high blood pressure) can also increase an individual's risk for developing the disease.
How is dementia diagnosed?
There is no single test that can diagnose dementia. Instead, doctors use a variety of tests and assessments to evaluate a person's cognitive function and rule out other possible causes of their symptoms. These tests may include physical exams, cognitive assessments, blood tests, brain imaging scans, and other diagnostic tools.
How can I reduce my risk of developing dementia?
While there is no surefire way to prevent the development of all types of dementia, research has shown that certain lifestyle choices may help reduce an individual's risk. These include staying physically active, eating a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, maintaining social connections with others, engaging in mentally stimulating activities (such as puzzles or games), getting enough sleep each night, and managing other health conditions such as high blood pressure or diabetes.
Summary
Dementia is a complex and challenging disease that affects millions of people worldwide. The statistics presented in this article underscore the need for increased awareness, research, and investment to address the impact of dementia on individuals, families, and society as a whole. By working together, we can improve the lives of people with dementia and their caregivers and advance our understanding of this devastating disease.
Sources:
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia
- https://www.alzint.org/about/dementia-facts-figures/dementia-statistics/
- https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/facts-figures
- https://www.cdc.gov/aging/publications/features/Alz-Greater-Risk.html
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
- https://www.alzint.org/about/dementia-facts-figures/
- https://www.cdc.gov/aging/dementia/index.html
- https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanpub/article/
- https://alzheimer.ca/en/about-dementia/what-dementia/dementia-numbers-canada