The Importance Of Dementia Care Plan
Unlock the power of a dementia care plan for your loved ones. Discover the benefits, challenges, and resources to enhance their quality of life.
Understanding Dementia Care Planning
When it comes to providing care for individuals with dementia, a comprehensive dementia care plan plays a crucial role in ensuring their well-being and quality of life. This section will explore the importance of dementia care planning and the availability of Medicare reimbursement for such planning.
Importance of Dementia Care Planning
Dementia care planning is essential for individuals experiencing cognitive decline, including Alzheimer's disease and other dementias. It involves creating a personalized plan that addresses the unique needs of each individual. By engaging in in-depth care planning, individuals with dementia can benefit from a higher quality of life and improved outcomes.

A well-structured dementia care plan helps caregivers and healthcare professionals identify and address the specific challenges faced by individuals with dementia. It provides guidance on managing symptoms, enhancing safety measures, ensuring proper nutrition, and addressing emotional and psychological well-being. With a comprehensive care plan in place, individuals with dementia can receive the necessary support and interventions tailored to their specific needs.
Medicare Reimbursement for Dementia Care Planning
It is important to note that Medicare covers the cost of dementia care planning under certain conditions. Reimbursement for dementia care planning falls under CPT® code 99483, which provides a reimbursement for clinical visits resulting in a comprehensive care plan. Clinicians eligible for reimbursement under this code include physicians, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, clinical nurse specialists, and certified nurse midwives.
The reimbursement for dementia care planning recognizes the value and importance of providing comprehensive care for individuals with dementia. It allows healthcare professionals to dedicate the necessary time and resources to develop and implement personalized care plans for their patients. This reimbursement not only supports the delivery of high-quality care but also contributes to better outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals with dementia and their caregivers.
To ensure ongoing and effective care, it is recommended that a formal update to the care plan occurs at least once per year or when indicated by disease progression. Sharing the care plan with the patient and/or caregiver during the initial education and support session is crucial. Documentation of this discussion is also essential in the clinical note for all encounters billed under CPT code 99483.
In conclusion, dementia care planning plays a vital role in providing comprehensive and personalized care for individuals with dementia. It allows healthcare professionals to address the specific challenges and needs of individuals with dementia, ultimately improving their quality of life. The availability of Medicare reimbursement for dementia care planning further emphasizes the significance of this approach in delivering effective care and support to individuals with dementia and their caregivers.
Early Diagnosis and its Benefits
Recognizing the signs of dementia and obtaining an early diagnosis is crucial for both individuals and their caregivers. Early diagnosis brings numerous benefits, including improved understanding of the condition, better planning for the future, and access to appropriate support and resources. Let's explore the benefits of early diagnosis for individuals and caregivers.
Benefits of Early Diagnosis for Individuals
An early diagnosis of dementia allows individuals to become actively involved in personal decisions, including healthcare, and assert their rights. It provides an opportunity to gain a better understanding of the condition and set realistic expectations for the future. With this knowledge, individuals can make informed decisions about legal, financial, and care matters and communicate their wishes to family and friends.
Early diagnosis also allows individuals to take advantage of local resources and programs offered by organizations like the Alzheimer Society. These resources provide information, support, and education to help individuals learn how to live well with dementia. Furthermore, timely treatment, including medications and alternative therapies, can be initiated early in the disease process, potentially offering the most effective outcomes [1].
Benefits of Early Diagnosis for Caregivers
Early diagnosis not only benefits individuals with dementia but also their caregivers. It allows caregivers to better understand the condition and plan for the future, reducing uncertainty and stress. With an early diagnosis, caregivers can access support services and educational resources that provide guidance on how to care for someone with dementia. This support helps caregivers develop the necessary skills and knowledge to provide effective care and support their loved ones.
Moreover, early diagnosis enables caregivers to participate in shared decision-making with the person with dementia, ensuring that the individual's preferences and wishes are respected. Caregivers can assist in making informed decisions about medical treatments, care options, and end-of-life planning, ensuring that the person with dementia receives care aligned with their wishes.
By obtaining an early diagnosis, individuals and caregivers can access the necessary resources, support, and treatments to enhance the quality of life for the person with dementia and reduce the burden on caregivers. Early intervention and management strategies can help stabilize cognitive decline, prevent additional functional disability, and address behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia. Together, early diagnosis and proactive care planning contribute to a more positive and supportive journey for both individuals and caregivers.
Components of a Comprehensive Dementia Care Plan
A comprehensive dementia care plan is essential for providing appropriate and effective care for individuals with dementia. It involves various components that address the unique needs and challenges associated with cognitive decline. The following sections outline the key components of a comprehensive dementia care plan.
Initial Assessment and Education
The first step in developing a dementia care plan is conducting an initial assessment. This assessment involves a comprehensive evaluation of the individual's cognitive abilities, functional status, and overall health. It helps identify the specific areas of concern and sets a baseline for monitoring progress.
During the initial assessment, it is crucial to provide education and support to the patient and/or caregiver. This education should cover essential topics such as understanding dementia, managing symptoms, and promoting a safe and supportive environment. By providing education early on, individuals and caregivers can gain a better understanding of the condition, which can help reduce anxiety and improve overall management of the disease [3].
Neuropsychiatric Symptom Management
Neuropsychiatric symptoms, such as agitation, aggression, depression, and anxiety, are common in individuals with dementia. Addressing these symptoms is crucial for improving the individual's quality of life and reducing caregiver burden. A comprehensive dementia care plan should include strategies for managing these symptoms effectively.
Management of neuropsychiatric symptoms may involve a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches. Non-pharmacological interventions, such as behavioral and environmental modifications, can be highly effective in reducing symptom severity and improving overall well-being. Pharmacological interventions should be considered when non-pharmacological approaches alone are insufficient. However, it's important to carefully evaluate the potential risks and benefits of medication use in individuals with dementia.
Referrals to Community Resources
A comprehensive dementia care plan should include referrals to community resources that can provide additional support and services to individuals and their caregivers. These resources may include support groups, respite care, home health services, and memory care programs. Referring individuals to these resources helps ensure that they have access to the necessary assistance and can benefit from the expertise of professionals experienced in dementia care.
The Alzheimer's Association provides a comprehensive toolkit with validated measures and assessment tools to assist clinicians in conducting dementia care planning visits. This toolkit includes resources for cognitive assessment, safety assessment, caregiver profiling, end-of-life screening, and additional patient and caregiver resources.
By including these components in a comprehensive dementia care plan, healthcare providers can improve the overall management of dementia and enhance the well-being of individuals and their caregivers. The combination of initial assessment and education, neuropsychiatric symptom management, and referrals to community resources ensures a holistic approach to dementia care and supports a higher quality of life for those living with dementia.
Tools and Resources for Dementia Care Planning
Dementia care planning involves a range of considerations and assessments to ensure comprehensive care for individuals with dementia. Fortunately, there are various tools and resources available to support caregivers and healthcare professionals in this process.
Alzheimer's Association Toolkit
The Alzheimer's Association provides a comprehensive toolkit with validated measures and assessment tools to assist clinicians in conducting dementia care planning visits. This toolkit equips healthcare professionals with a wide range of resources to support the care of individuals with dementia.
Within the toolkit, you can find resources for cognitive assessment and care planning services, safety assessment, caregiver profiling, end-of-life screening, and additional patient and caregiver resources. These tools help clinicians gather essential information and tailor care plans to meet the specific needs of individuals with dementia.
Validated Measures and Assessment Tools
As part of dementia care planning, healthcare professionals rely on validated measures and assessment tools to evaluate cognitive function, track disease progression, and assess the overall well-being of individuals with dementia. These tools provide valuable insights and assist in developing personalized care plans.
Some commonly used validated measures and assessment tools include:
These tools assist healthcare professionals in gaining a comprehensive understanding of an individual's cognitive abilities, behavior, and overall functioning, which in turn informs the development of an effective care plan.
Caregiver and Patient Resources
Caregivers play a vital role in dementia care planning, and it is essential to provide them with the necessary resources and support. The Alzheimer's Association and other organizations offer a range of caregiver and patient resources to help navigate the challenges associated with dementia care.
These resources may include educational materials, support groups, online forums, and helplines. They provide valuable information, guidance, and emotional support to caregivers, helping them cope with the demands of caregiving and enhance their ability to provide quality care.
By utilizing these tools and resources, caregivers and healthcare professionals can collaborate effectively in developing and implementing a comprehensive dementia care plan. These resources offer valuable support, enhance the quality of care provided, and improve the overall well-being of individuals with dementia and their caregivers.
Challenges Faced by Individuals with Dementia and Caregivers
Caring for individuals with dementia comes with unique challenges that both the individuals and their caregivers must navigate. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for providing the best possible care and support. Here, we explore three common challenges faced by individuals with dementia and their caregivers: wandering and safety concerns, agitation and anxiety, and poor nutrition and meal preparation.
Wandering and Safety Concerns
Wandering is a common challenge experienced by individuals with dementia, affecting approximately six in every ten people with Alzheimer's disease [4]. Wandering can occur at various stages of the disease and poses safety risks. Individuals may become disoriented and wander away from familiar surroundings, putting themselves at risk of getting lost or encountering dangerous situations.
To address wandering and safety concerns, it is important to take preventative measures. Ensuring that the individual carries identification at all times can help in case they become lost. Additionally, planning and implementing strategies to eliminate driving responsibilities can help mitigate the risks associated with wandering.
Agitation and Anxiety
Agitation and anxiety are common mood disruptions experienced by individuals with dementia at all stages of the disease's progression. These disruptions can significantly impact the individual's ability to carry out daily tasks and interact with others. It is essential to seek help from a physician when mood disruptions interfere with the individual's overall well-being and daily activities.
Caregivers should provide a calm and soothing environment, minimize triggers that may cause agitation, and engage the individual in activities that promote relaxation and enjoyment. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage severe agitation and anxiety, but these should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Poor Nutrition and Meal Preparation
As dementia progresses, poor nutrition becomes a significant challenge. Memory loss and cognitive decline can make meal preparation and eating independently difficult for individuals with dementia. This can result in weight loss, decreased immune response, and healing issues.
Addressing poor nutrition concerns involves finding practical solutions. Signing up for services like Meals on Wheels or community meal sites can provide nutritious meals and ensure that individuals with dementia are receiving proper nutrition. Additionally, caregivers can simplify mealtime routines, provide finger foods or easily manageable meals, and offer gentle reminders to encourage eating.
Understanding and addressing these challenges are vital for supporting individuals with dementia and their caregivers. By implementing strategies to address wandering and safety concerns, managing agitation and anxiety, and addressing poor nutrition challenges, caregivers can enhance the quality of life for individuals with dementia and provide the necessary support they need.
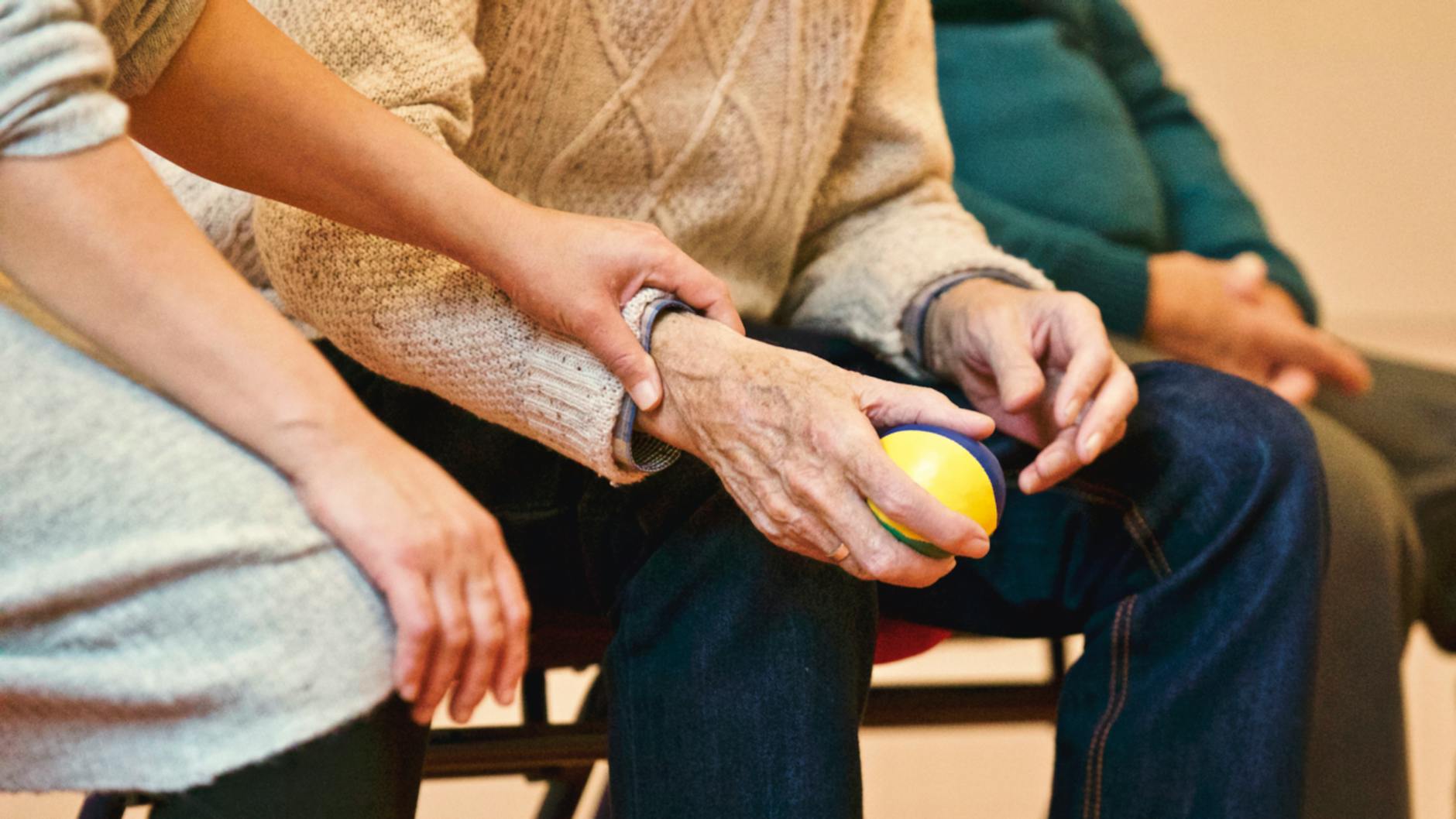
The Role of Caregivers in Memory Care
When it comes to memory care, caregivers play a crucial role in supporting individuals with dementia and memory impairments. They provide the necessary assistance, compassion, and care to ensure the well-being and quality of life for those under their care. In this section, we will explore the key responsibilities of caregivers in memory care, including emotional and psychological support, daily care and assistance, as well as medical monitoring and medication management.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Caregivers in memory care are essential in providing emotional and psychological support to individuals with dementia. They create a safe and empathetic environment that promotes healing and a sense of belonging. By offering companionship, active listening, and reassurance, caregivers help individuals navigate the emotional challenges that often accompany memory impairments.
Furthermore, caregivers provide a familiar and comforting presence, helping individuals feel more secure and reducing feelings of anxiety or confusion. They engage in meaningful conversations, reminiscing, and activities that stimulate cognitive function and improve overall well-being.
Daily Care and Assistance
Caregivers in memory care are responsible for providing daily care and assistance to individuals with memory impairments. This includes helping with activities of daily living such as bathing, dressing, grooming, and eating. By offering patient and compassionate support, caregivers ensure that individuals are comfortable and maintain their dignity.
In addition, caregivers help individuals with memory impairments navigate their daily routines, assisting with medication reminders, meal preparation, and managing household tasks. They create structured and predictable environments, promoting a sense of familiarity and reducing confusion.
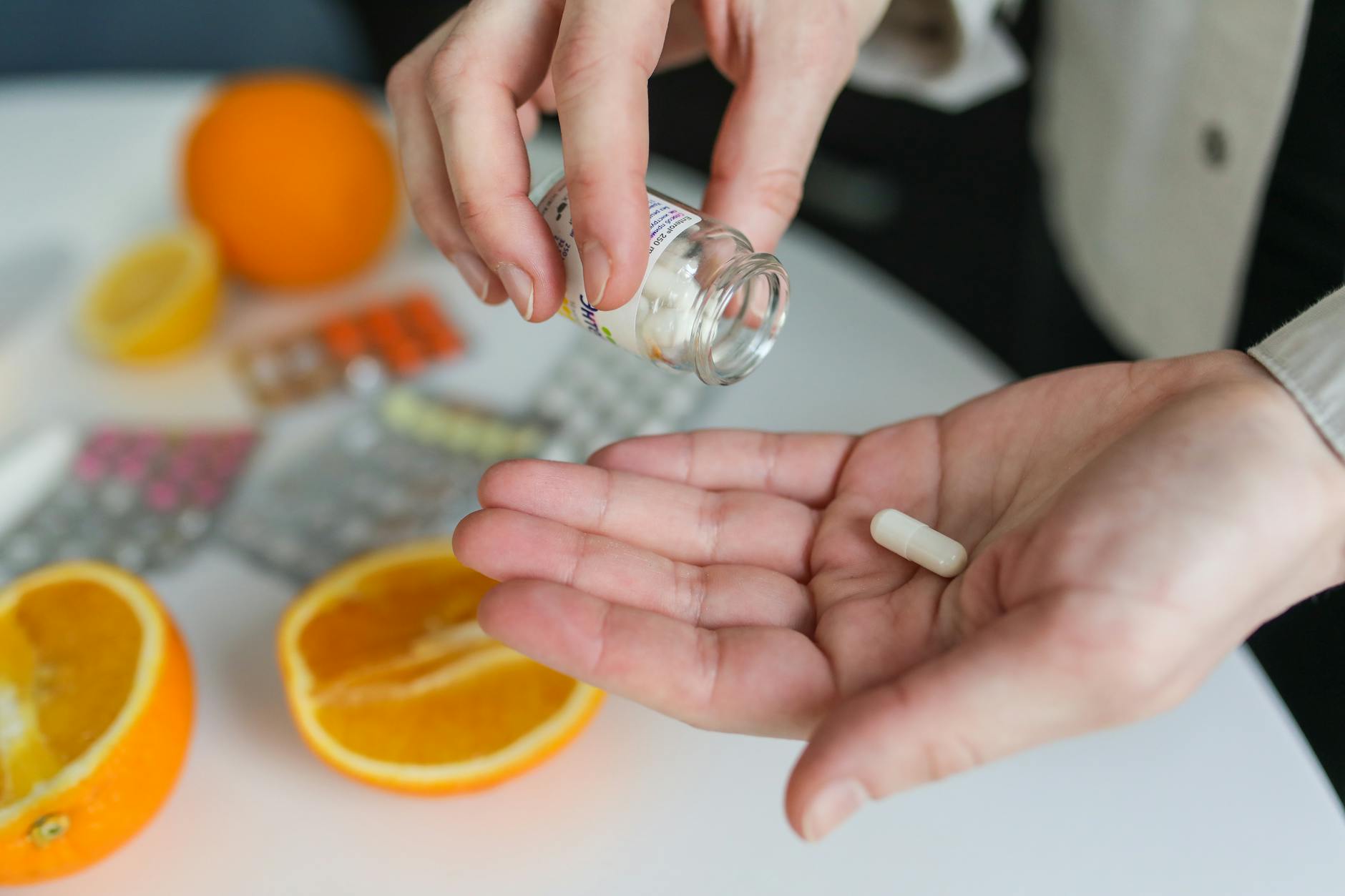
Medical Monitoring and Medication Management
Caregivers in memory care are responsible for the medical monitoring and medication management of individuals with dementia. They work closely with healthcare professionals to ensure that individuals receive the necessary care and treatment for their specific needs. This includes monitoring vital signs, observing any changes in health, and promptly reporting concerns to healthcare providers.
Furthermore, caregivers play a vital role in ensuring individuals adhere to their medication schedules. They assist with medication administration, track medication effectiveness, and monitor any potential side effects. By maintaining accurate medication records, caregivers contribute to the overall well-being and safety of individuals in memory care.
In summary, caregivers in memory care have a multifaceted role in providing support and care for individuals with dementia and memory impairments. They offer emotional and psychological support, assist with daily activities, and ensure medical monitoring and medication management. The dedication and commitment of caregivers greatly contribute to the quality of life and well-being of individuals in memory care settings.
The Impact of Dementia on Individuals and Society
Dementia, a condition characterized by a decline in cognitive abilities, has a significant impact on both individuals and society as a whole. Understanding the global prevalence, economic and healthcare costs, and addressing the challenges associated with dementia are crucial for improving the quality of life for those affected.
Global Prevalence and Projections
The number of people worldwide living with dementia is staggering. Currently, an estimated 44.4 million individuals are affected by this condition, which is projected to increase to 75.6 million in 2030 and a staggering 135.5 million in 2050 [2]. The aging population plays a significant role in these projections, as the proportion of the world's population aged over 60 years is expected to more than treble between 2000 and 2050, from 605 million to 2 billion. These numbers highlight the urgent need for effective dementia care and support.
Economic and Healthcare Costs
The economic and healthcare costs associated with dementia are substantial. Medicare recipients with dementia currently account for 34% of Medicare spending, despite constituting only 13% of the total Medicare beneficiaries [6]. By 2050, it is projected that Medicare will spend over $1 trillion on beneficiaries with dementia [6]. These costs encompass various aspects, including medical care, long-term care, and support services.
Moreover, dementia not only impacts healthcare systems but also places a significant burden on families and caregivers. The demands of providing care for individuals with dementia can be physically, emotionally, and financially challenging. Caregivers often face increased stress, disrupted employment, and financial strain. Recognizing and addressing these challenges is vital to ensure adequate support for both individuals with dementia and their caregivers.
Addressing Challenges and Improving Quality of Life
To address the challenges posed by dementia and improve the quality of life for individuals with the condition, a comprehensive approach is necessary. Successful management of dementia requires interventions that target both cognitive and functional symptoms. This can involve a combination of pharmacological therapies and psychosocial interventions that address the entire spectrum of dementia symptomatology, including cognitive decline, functional disability, and behavioral and psychological symptoms.
Furthermore, early diagnosis and intervention play a crucial role in improving outcomes for individuals with dementia. Early diagnosis allows for timely access to appropriate care, support, and treatment options. It also enables individuals and their families to plan for the future and make informed decisions about their care.
In conclusion, the impact of dementia on individuals and society is profound. The increasing prevalence, economic costs, and healthcare burden associated with this condition necessitate a comprehensive and proactive approach to dementia care. By addressing the challenges faced by individuals with dementia and their caregivers, and by promoting early diagnosis and intervention, we can strive towards improving the quality of life for those affected by this complex condition.
References
[2]:
[3]:
[4]:
[5]:
[6]: