Assisted Living vs. Long-Term Care: Making The Right Choice
Assisted living vs. long-term care: Which is right for your loved one? Explore options, costs, and considerations for making the best choice.

Understanding Assisted Living and Long-Term Care
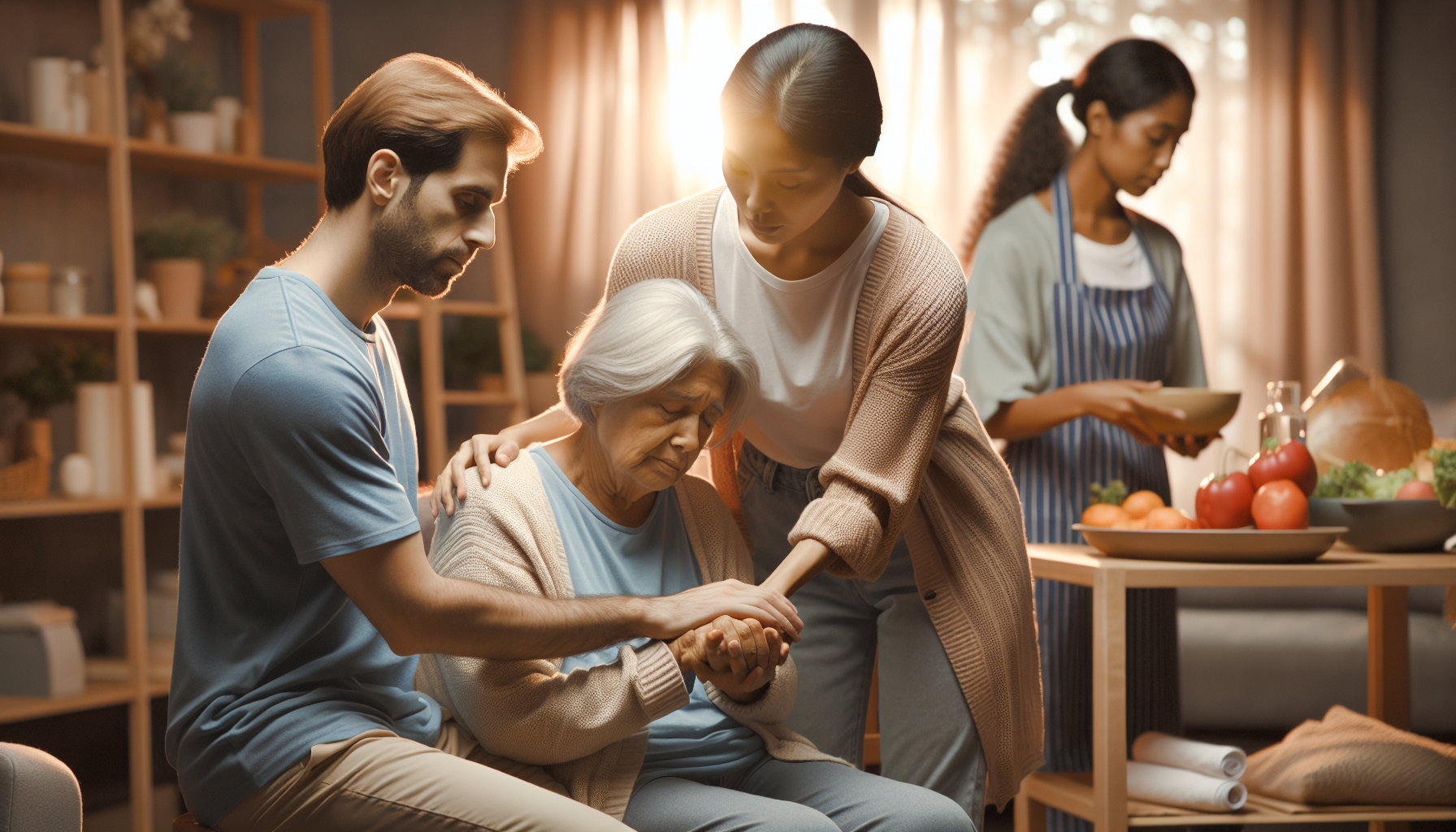
When it comes to caring for elderly loved ones, choosing the right living arrangement is crucial. Assisted living and long-term care are two options that provide different levels of support and services. It's important to understand the differences between these options and consider various factors when making a decision.
The Difference Between Assisted Living and Nursing Homes
Assisted living facilities cater to individuals who require assistance with daily care but do not need as much help as provided in a nursing home. These facilities typically range in size from 25 to over 100 residents and offer services such as meals, personal care assistance, medication help, housekeeping, laundry, supervision, security, and social activities. However, it's important to note that residents usually pay for these costs themselves, as Medicare does not cover assisted living expenses [1]. Assisted living communities provide a more independent lifestyle with varying levels of care and support, including help with daily tasks.

On the other hand, nursing homes, also known as long-term care facilities, are more suitable for seniors who require 24-hour nursing care and significant assistance with daily activities. Nursing homes provide skilled nursing care and typically include professional medical services. They are designed for individuals who have chronic conditions or disabilities that require around-the-clock medical care and supervision. While assisted living communities offer a more independent lifestyle, long-term care facilities focus on providing comprehensive medical and nursing services.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Assisted Living and Long-Term Care
When deciding between assisted living and long-term care, several factors should be taken into account. These include the level of care needed, the individual's medical conditions, and their overall preferences.
Assisted living is best suited for individuals who need some help with daily activities but are still mostly independent. It provides a supportive environment where residents can maintain their independence while receiving assistance as needed. Long-term care, on the other hand, is more appropriate for those who require around-the-clock medical care and supervision due to chronic conditions or disabilities. It offers a higher level of medical services and skilled nursing care.
Other factors to consider include the individual's social needs, personal preferences, and financial considerations. Assisted living facilities often provide a range of social activities and amenities to promote engagement and well-being. Long-term care facilities prioritize medical care and may have a more clinical environment.
Ultimately, the decision between assisted living and long-term care should be based on a thorough assessment of the individual's needs, preferences, and the level of care required. It's important to consult with healthcare professionals, family members, and the individual themselves to ensure that the chosen option aligns with their specific circumstances.
By understanding the differences between assisted living and long-term care and considering the relevant factors, families and caregivers can make an informed decision that provides the best possible care and support for their loved ones.
Assisted Living: Independence and Support
When considering the options for senior care, it's important to understand the difference between assisted living and long-term care facilities. Assisted living facilities are designed for seniors who need some help with activities of daily living, such as bathing, dressing, medication management, and meals. On the other hand, long-term care facilities, often referred to as nursing homes, are more appropriate for seniors who require 24-hour nursing care and significant assistance with daily activities.
Services and Amenities in Assisted Living Facilities
Assisted living communities offer a more independent lifestyle with varying levels of care and support. These facilities provide a range of services and amenities to cater to the needs of their residents. Some common services and amenities found in assisted living facilities include:
Assisted living facilities aim to create a sense of community and independence for their residents while offering assistance with daily tasks. They provide a more home-like environment compared to long-term care settings, allowing seniors to maintain their privacy and autonomy.
Cost Comparison: Assisted Living vs. Nursing Homes
When considering the financial aspect of senior care, it's important to compare the costs of assisted living and long-term care facilities. The cost of care can vary depending on factors such as location, level of care needed, and amenities provided.
In general, assisted living tends to be less expensive compared to long-term care facilities, primarily due to the level of care and medical services provided. However, it's important to note that costs can vary significantly depending on the specific facility and its location.
To provide a general comparison, the table below outlines the average monthly costs for assisted living and nursing homes in the United States:
Figures courtesy Village Green Senior Living
It's important to note that these figures are approximate and can vary depending on factors such as location, level of care needed, and additional services or amenities provided by the facility. It's recommended to research and gather specific cost information from individual facilities to make an informed decision.
By understanding the services, amenities, and costs associated with assisted living facilities, families and caregivers can make the right choice for their loved ones. Assisted living offers a balance between independence and support, providing a community-focused environment with the necessary assistance for daily living tasks.
Long-Term Care: Skilled Nursing and Medical Services
When it comes to long-term care, facilities that provide skilled nursing and medical services play a crucial role in meeting the needs of individuals with complex medical conditions or those requiring specialized care over an extended period of time.
Medical Care and Services in Long-Term Care Facilities
Long-term care facilities, such as nursing homes or skilled nursing facilities, offer a higher level of medical care compared to assisted living facilities. These facilities are equipped to handle complex medical needs and provide services such as skilled nursing care, medication management, and therapy services [3]. The staff-to-resident ratio is higher in long-term care facilities, ensuring that residents receive the necessary medical attention and support for their conditions.
In addition to round-the-clock nursing care, long-term care facilities often offer specialized services like physical, occupational, and speech therapy. These services aim to improve residents' physical functioning, enhance their independence, and provide support for conditions such as Alzheimer's disease.
Cost Comparison: Long-Term Care vs. Assisted Living
While the cost of long-term care facilities varies depending on factors such as location and level of care required, it is generally higher than the cost of assisted living. The increased level of medical care and specialized services provided in long-term care facilities contribute to the higher costs.
It's important to note that Medicare generally does not cover long-term stays in nursing homes, but Medicaid may provide coverage for some costs depending on eligibility. Long-term care insurance policies may also offer coverage for nursing home care.
When considering the cost of long-term care versus assisted living, it's essential to assess the specific needs of your loved one and consider the level of care required. Long-term care facilities are designed for individuals with more significant medical needs, while assisted living facilities focus on providing support with daily activities and fostering independence.
By understanding the medical care and services offered in long-term care facilities, as well as the associated costs, you can make informed decisions about the most suitable option for your loved one's long-term care needs. It is always advisable to consult with healthcare professionals and explore the specific offerings of different facilities to ensure the best possible care for your loved one.
Choosing the Right Option
When it comes to deciding between assisted living and long-term care, it's essential to assess the needs of your loved one and consider the legal and financial aspects involved.
Assessing the Needs of Your Loved One
To make the right choice, it's crucial to evaluate the specific needs of your loved one. Assisted living facilities are ideal for individuals who require assistance with daily care but do not need 24-hour supervision or skilled nursing care. These facilities provide services such as meals, personal care assistance, medication help, housekeeping, laundry, supervision, security, and social activities. They are suitable for individuals who need some help with daily activities but are still mostly independent.
On the other hand, long-term care facilities offer a higher level of medical care than assisted living. They provide skilled nursing care, medication management, therapy services, and specialized care for conditions like Alzheimer's disease. Long-term care is more suitable for individuals with chronic medical conditions or those who need specialized care over an extended period of time.
Consider your loved one's specific health conditions, mobility, and level of independence when assessing their needs. It may be helpful to consult with their healthcare providers to gain a better understanding of the level of care required.
Legal and Financial Considerations
When choosing between assisted living and long-term care, it's important to consider the legal and financial aspects. Assisted living facilities are typically paid for out-of-pocket by residents themselves, as Medicare does not cover assisted living expenses. The costs of assisted living can vary depending on the location, services, and amenities provided.
On the other hand, long-term care facilities often involve higher costs due to the level of medical care provided. Some individuals may be eligible for coverage through Medicare or Medicaid for long-term care services, but it's important to understand the specific requirements and limitations of these programs.
Before making a decision, it's advisable to consult with an elder law attorney or financial advisor who specializes in long-term care planning. They can provide guidance on legal and financial matters, including understanding available resources, exploring insurance options such as long-term care insurance, and optimizing financial plans to ensure the best possible care for your loved one.
By carefully assessing the needs of your loved one and considering the legal and financial aspects, you can make an informed decision between assisted living and long-term care. Remember to involve your loved one in the decision-making process, taking their preferences and desires into account. Together, you can select the option that provides the necessary care, support, and quality of life for your loved one's specific situation.
Other Options for Long-Term Care
When considering long-term care options for your loved one, it's important to explore all available choices to find the best fit for their needs. In addition to assisted living and nursing homes, there are other options worth considering: continuing care retirement communities (CCRCs) and board and care homes.
Continuing Care Retirement Communities (CCRCs)
Continuing Care Retirement Communities (CCRCs) offer a range of services and care levels within a single location, making them an attractive option for many seniors. These communities provide independent housing, assisted living, and skilled nursing care, allowing residents to transition seamlessly between different levels of care as their needs evolve [1].
CCRCs often charge a one-time entrance fee along with a monthly fee. While individuals typically cover most of these costs themselves, certain services may be covered by Medicare, Medicaid, or long-term care insurance, depending on the level of care provided.
Board and Care Homes
Board and care homes are small private facilities that provide personal care and meals to a limited number of residents, usually 20 or fewer. These homes do not typically offer nursing or medical care, focusing instead on providing a homelike environment and support with daily activities [1]. Residents in board and care homes generally bear the costs of living there, as Medicare does not cover these expenses.
When considering board and care homes, it's essential to assess the specific needs of your loved one. If they require more intensive medical or nursing care, a different long-term care option may be more suitable. However, for individuals seeking a smaller, more intimate setting with personalized care, board and care homes can provide a comfortable and nurturing environment.
As with any long-term care decision, it's important to consider the financial implications. Costs can vary depending on the location, level of care, and additional services provided. It's advisable to consult with a financial advisor or explore available financial assistance options, such as Medicare, Medicaid, or long-term care insurance, to determine the best course of action for your loved one's specific situation.
By considering continuing care retirement communities (CCRCs) and board and care homes, you can expand your options and find the most suitable long-term care solution for your loved one. Each option offers unique advantages and services, allowing you to tailor the care to their specific needs and preferences.
Financing Long-Term Care
When considering long-term care options such as assisted living and nursing homes, it's important to understand the financial aspects involved. Financing long-term care can be a significant concern for families and caregivers of elderly individuals. Two potential sources of coverage for long-term care expenses are Medicare and Medicaid, as well as long-term care insurance.
Medicare and Medicaid Coverage
Medicare, the federal health insurance program for individuals aged 65 and older, generally does not cover long-term stays in nursing homes. However, it may pay for certain related costs such as doctor services and medical supplies. Medicaid, on the other hand, is a joint federal and state program that provides health coverage to eligible individuals with limited income and resources. Medicaid may cover some nursing home costs for those who meet the income and personal resources criteria.
For individuals who require long-term care, Medicaid or long-term care insurance may be options to cover the costs of nursing homes. It's important to note that Medicaid eligibility criteria may vary by state, and not all nursing homes accept Medicaid. Therefore, it's advisable to consult with local Medicaid offices and nursing homes for specific details and availability of coverage.
Long-Term Care Insurance
Long-term care insurance is a policy that provides coverage for long-term care services, including assistance with activities of daily living (ADLs) and care in various settings such as nursing homes and assisted living facilities. The coverage provided by long-term care insurance can vary between policies, so it's important to review the terms and conditions of each policy.
Some long-term care insurance policies may also provide partial coverage for assisted living expenses. However, not all policies include this coverage, so it's recommended to check with the insurance company for specific details on what services are covered. It's important to consider factors such as the cost of the policy, coverage limits, waiting periods, and any exclusions or restrictions that may apply.
It's worth noting that assisted living facilities are typically paid for using personal finances or long-term care insurance. Medicare generally does not cover the costs of assisted living, although Medicaid may provide coverage for some aspects depending on eligibility. Additionally, the cost of assisted living can vary depending on factors such as location, amenities, and level of care provided. It's advisable to research and compare costs to determine the most suitable option for your specific situation [4].
When navigating the financial aspects of long-term care, it can be helpful to consult with financial advisors, elder law attorneys, and insurance professionals who specialize in long-term care planning. They can provide guidance on available options and help determine the most appropriate financing strategy for your loved one's specific needs.
Making the Transition
Transitioning a loved one to a long-term care facility, whether it be assisted living or another type of care, can be a significant decision. Engaging with staff and monitoring care are crucial steps to ensure the well-being of your loved one during this transition. Additionally, planning and discussing preferences for care beforehand can help make the process smoother.
Engaging with Staff and Monitoring Care
Regular engagement with the staff at the long-term care facility is essential for staying informed about your loved one's well-being. Establishing open lines of communication allows you to address any concerns or questions you may have. By building a rapport with the staff, you can ensure that your loved one receives the attention and care they need.
Observation is key when monitoring your loved one's care. Regular visits and check-ins provide an opportunity to assess their overall well-being, both physically and emotionally. Look for signs of satisfaction, comfort, and a sense of belonging. Additionally, be vigilant for any changes in behavior, hygiene, or mobility. If you notice any concerning changes, address them with the staff promptly to ensure appropriate action is taken.
Planning and Discussing Preferences for Care
Planning for long-term care before it becomes necessary is crucial for making informed decisions and considering all available options. Discussing preferences for care with your loved one, family members, and legal advisors is recommended, especially for individuals with conditions like Alzheimer's disease or other types of dementia [5]. Understanding your loved one's preferences and wishes can guide the selection of the most suitable long-term care facility.
Having open and honest conversations about their preferences for care helps ensure that their needs and desires are met. Consider factors such as the level of assistance required, activities of daily living, social interactions, and any specific medical or personal requirements. By involving your loved one in the decision-making process, you empower them to have a sense of control and autonomy.
Planning for long-term care also involves considering the financial aspects. Long-term care can be expensive, and the payment sources vary depending on an individual's financial situation and eligibility for assistance programs. It's important to explore options such as personal funds, long-term care insurance, Medicaid, or other financial assistance programs. Consulting with financial advisors or specialists can provide valuable guidance in navigating the financial aspects of long-term care.
By engaging with staff, monitoring care, and planning ahead, you can ensure a smoother transition for your loved one into a long-term care facility. Regular communication and observation help maintain a high level of care, while open discussions about preferences for care provide a sense of dignity and respect. With proper planning and ongoing involvement, you can help create a positive and supportive environment for your loved one in their new home.
References
[2]:
[3]:
[4]:
[5]: